Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTRIC FIELD
CHHAYA PUBLICATION|Exercise SECTION RELATION QUESTIONS|50 VideosELECTRIC FIELD
CHHAYA PUBLICATION|Exercise HIGHER ORDER THINKING SKILL QUESTIONS|33 VideosELECTRIC ENERGY AND POWER
CHHAYA PUBLICATION|Exercise CBSE SCANNER|7 VideosELECTRIC POTENTIAL
CHHAYA PUBLICATION|Exercise CBSE Scanner|13 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CHHAYA PUBLICATION-ELECTRIC FIELD-CBSE SCANNER
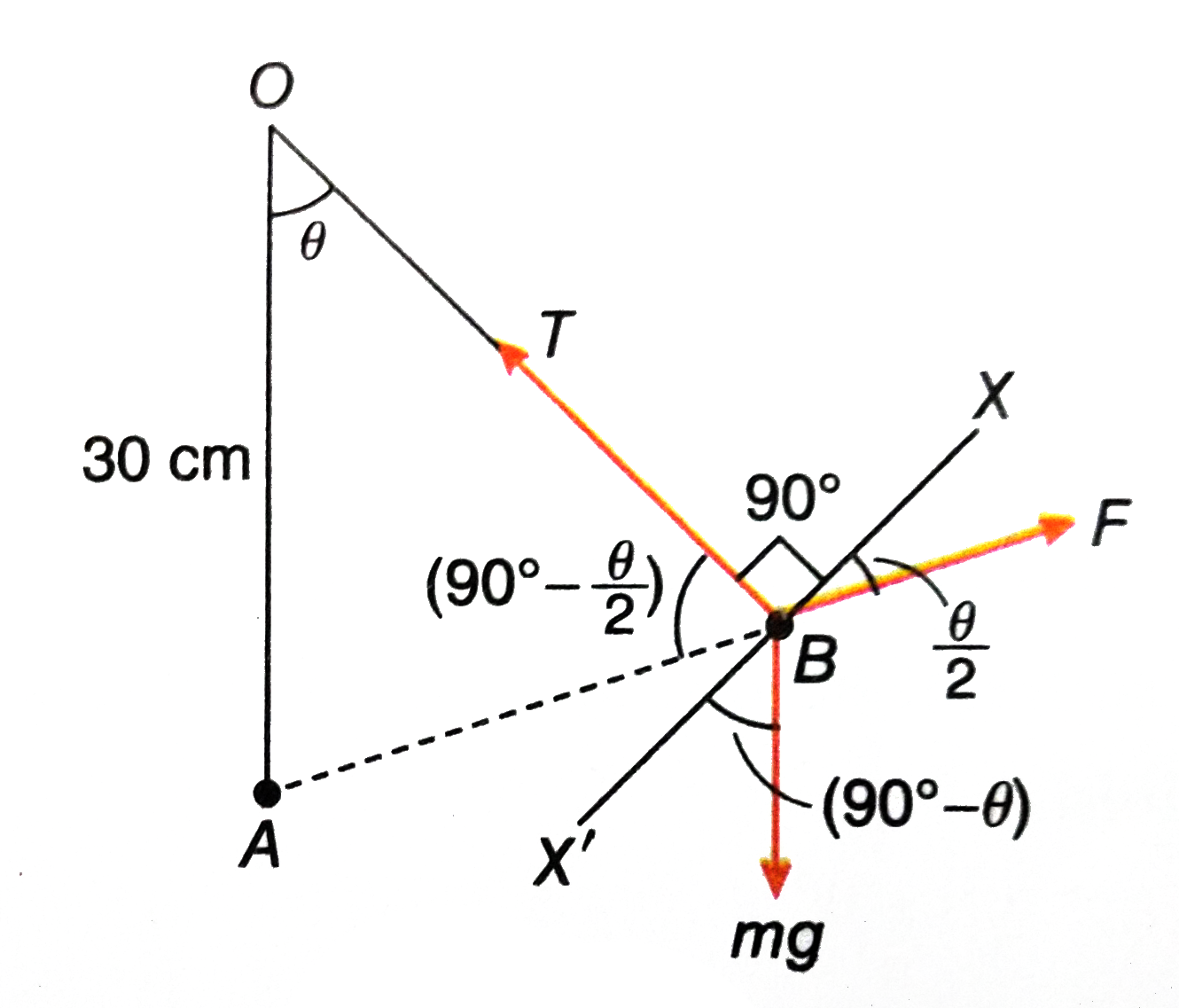
- A particle A having a charge of 5.0 xx 10^(-7)C is fixed in a vertica...
Text Solution
|
- A charge q is placed at the centre of a cube of side l. What is the el...
Text Solution
|
- An electric dipole is held in a uniform electric field. Show that th...
Text Solution
|
- An electric dipole is held in a uniform electric field. The dipole i...
Text Solution
|
- A charge q is placed at the centre of a cube. What is the electric flu...
Text Solution
|
- A charge q is placed at the centre of a cube. What is the electric flu...
Text Solution
|
- Define electric dipole moment. Is it a scalar or a vector? Derive the ...
Text Solution
|
- Two charges of magnitudes -2Q and +Q are located at points (a, 0) and ...
Text Solution
|
- Using Gauss' law deduce the expression for the electric field due to a...
Text Solution
|
- Using Gauss' law deduce the expression for the electric field due to a...
Text Solution
|
- Why do the electrostatic field lines not form closed loops?
Text Solution
|
- Deduce the expression for the torque acting on a dipole of dipole mome...
Text Solution
|
- Consider two hollow concentric spheres S(1) and S(2) enclosing charges...
Text Solution
|
- Consider two hollow concentric spheres S(1) and S(2) enclosing charges...
Text Solution
|
- A point charge +Q is placed in the vicinity of a conducting surface. T...
Text Solution
|
- Define electric electric flux. Write its SI unit.
Text Solution
|
- Using Gauss' law, obtain the electric flux due to a point charge q enc...
Text Solution
|
- Show that the electric field due to a uniformly charged infinite plane...
Text Solution
|
- What is the amount of work done in moving a point charge Q around a ci...
Text Solution
|
- Find the electric field intensity due to a uniformly charged spherical...
Text Solution
|
- Find the electric field intensity due to a uniformly charged spherical...
Text Solution
|