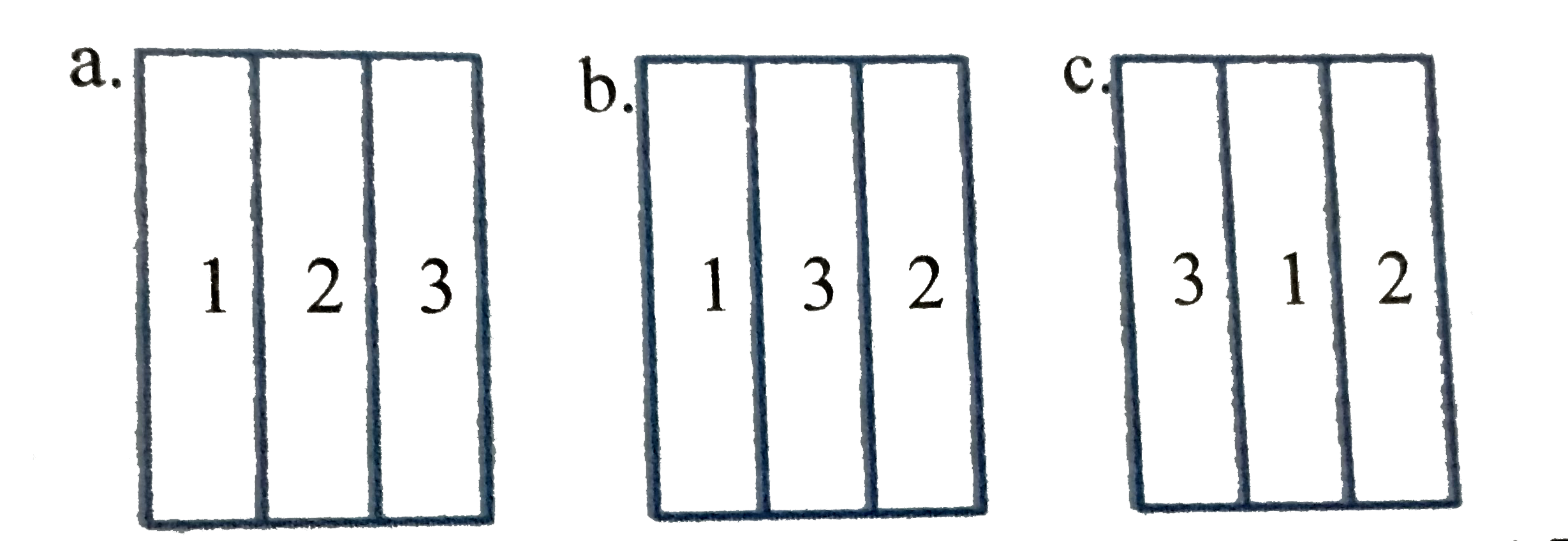
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
TRANSMISSION OF HEAT
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Comprehension type|3 VideosTRANSMISSION OF HEAT
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Fill in the blanks type|6 VideosTRANSMISSION OF HEAT
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Single correct|9 VideosTHERMODYNAMICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise 24|1 VideosTRAVELLING WAVES
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Integer|9 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems