Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ANURAG MISHRA-WORK AND ENERGY-Eample
- In the figure shown, the mass of the hanging block is m, while that of...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks having masses 8 kg and 16 kg are connected to the two ends...
Text Solution
|
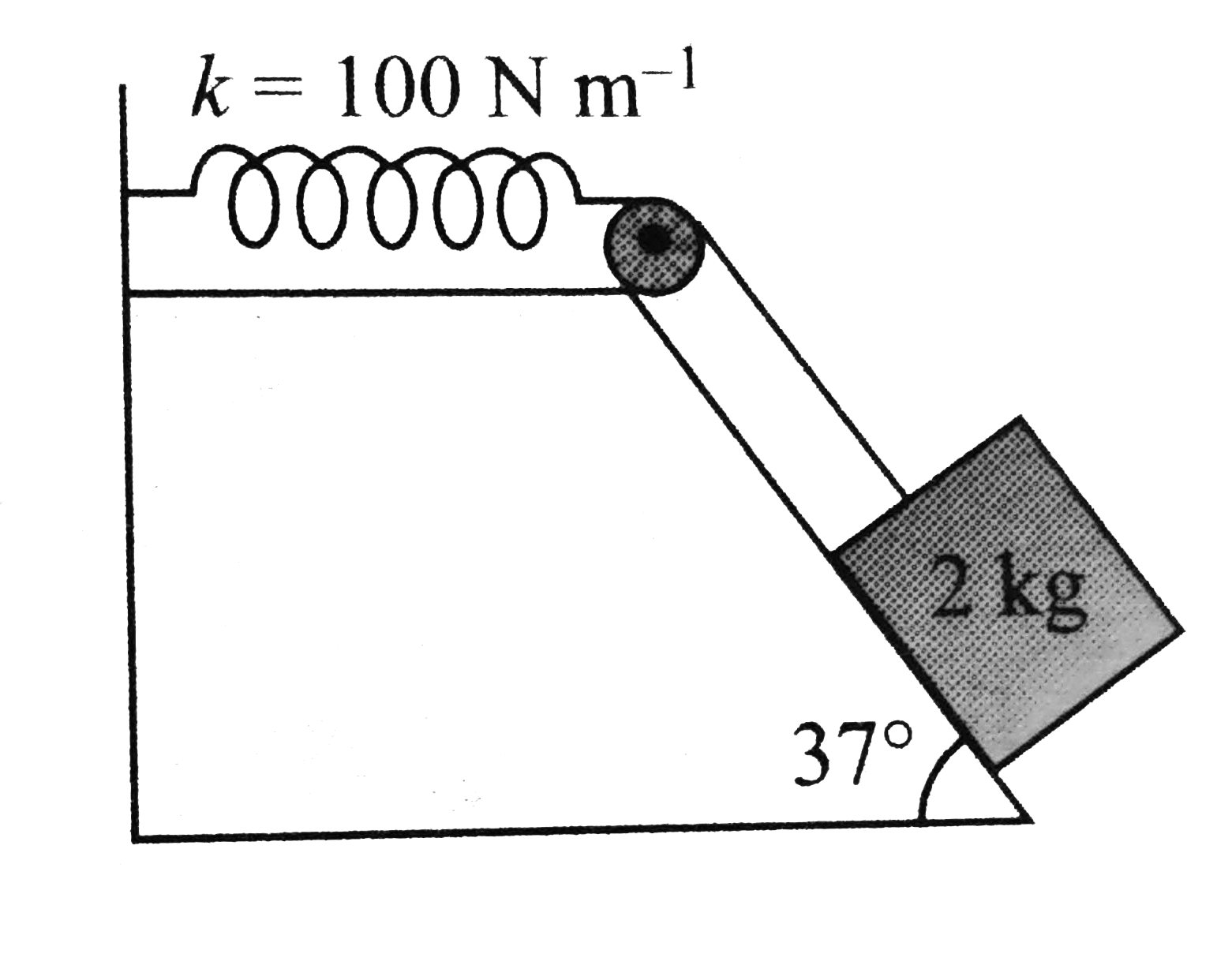
- a. A 2-kg situated on a smooth fixed incline is connected to a spring ...
Text Solution
|
- A ring of mass m=1kg can slide over a smooth vertical rod. A light str...
Text Solution
|
- From what minimum height hmust the system be released when spring is u...
Text Solution
|
- A pendulum bob of mass m and length L is released from angle theta wit...
Text Solution
|
- A boy throws a ball with initial velocity u at an angle of projection ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider an Atwood machine with both the masses at the same level as s...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m hangs an a vertical spring. Initially the spring is ...
Text Solution
|
- In Fig 3E.17, the mass m(2) rests on a rough table. The mass m(1) is p...
Text Solution
|
- The force 15 N pulls the lower block for 2m, find speed.
Text Solution
|
- Find velocity of A and B when A is about to touch the ground Also veri...
Text Solution
|
- m(A) = 1 kg, m(B) = 2 kg, m(C) = 10 kg
Text Solution
|
- If chain starts slipping find its KE when chain becomes completely str...
Text Solution
|
- Chain is on the verge of slipping, find the velocity of the chain, whe...
Text Solution
|
- Find how much m will rise if 4m falls away. Block are at rest and in e...
Text Solution
|
- Find velocity of ring when spring becomes horizontal
Text Solution
|
- A chain of mass m and length 1 lies on a rough table. The chain just s...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform chain of length 1 and mass m is kept on a smooth table. It i...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform chain of length of length pir lies inside a smooth semicircu...
Text Solution
|