A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Two ideal slits S(1) and S(2) are at a distance d apart, and illuninat...
Text Solution
|
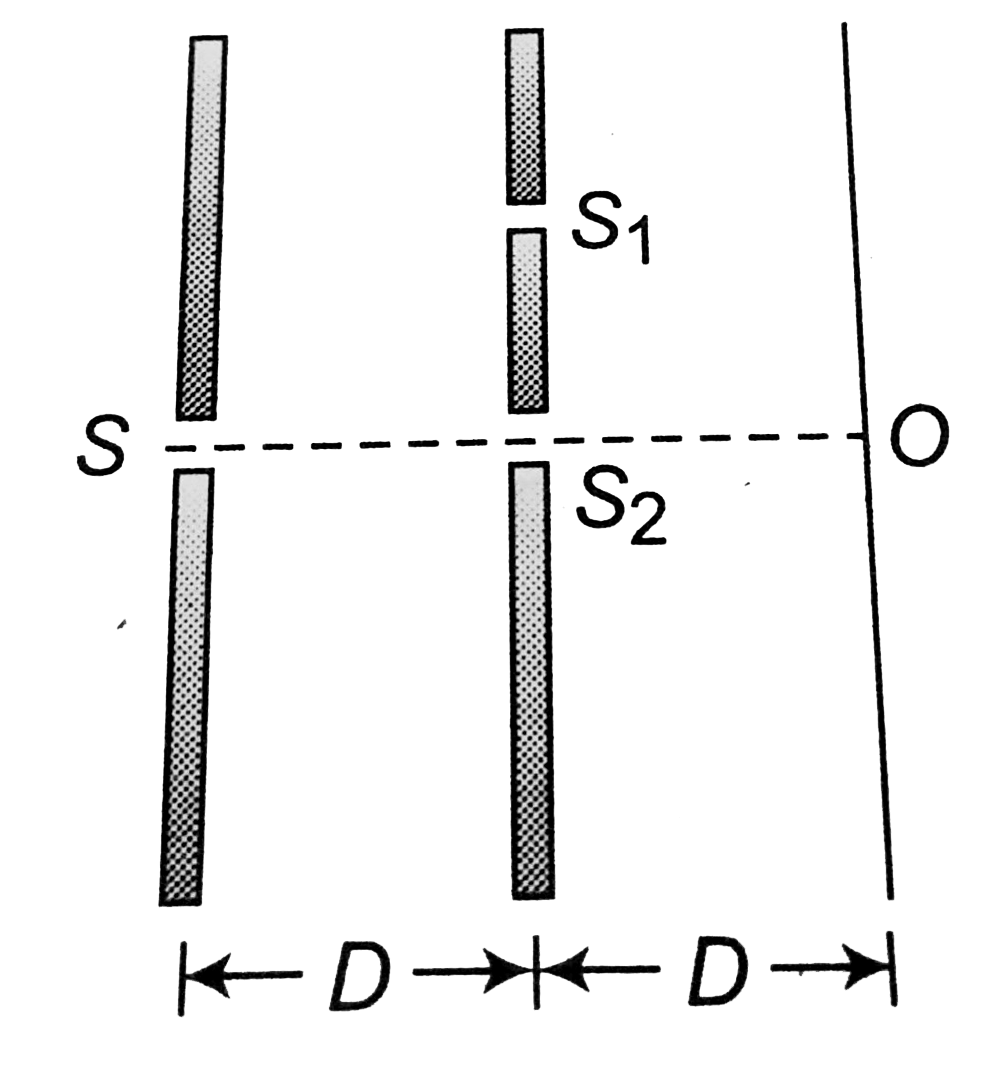
- Consider the situation shown in fig. The two slits S(1) and S(2) place...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the situation shown in fig. The two slits S(1) and S(2) place...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the situation shown in fig. The two slits S(1) and S(2) place...
Text Solution
|
- Two ideal slits S(1) and S(2) are at a distance d apart, and illuninat...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the situation shown in figure-6.35. The two slits S(1) and S(...
Text Solution
|
- In Young's double slit experiment the two slits are d distance apart....
Text Solution
|
- In a Young's double slit experiment, a monochromatic source of wavelen...
Text Solution
|
- In a Young's double slit experiment, a monochromatic source of wavelen...
Text Solution
|