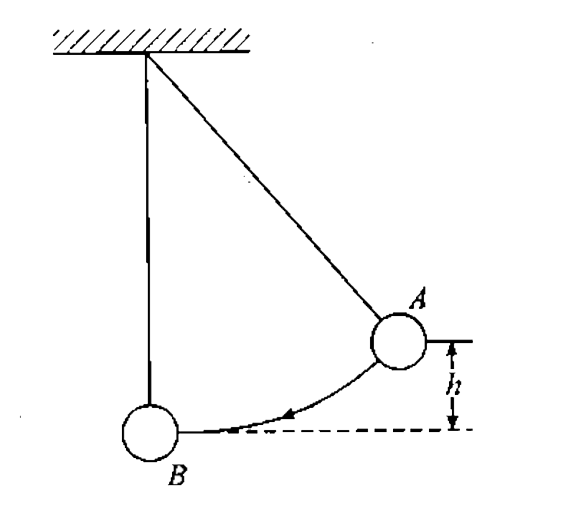
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
LINEAR MOMENTUM & ITS CONSERVATION
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA|Exercise Numerical MCQ s|75 VideosLINEAR MOMENTUM & ITS CONSERVATION
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA|Exercise Advance McQ|20 VideosLINEAR MOMENTUM & ITS CONSERVATION
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA|Exercise Discussio Q|28 VideosKINEMATICS
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA|Exercise Unsolved Numerical Pro.|83 VideosNEWTONS LAWS OF MOTION
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA|Exercise Unsolved Numerical Problem|81 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA-LINEAR MOMENTUM & ITS CONSERVATION-Conceptual MCQ s single option correct
- The velocities in a head on elastic collision be interchanged"
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass m moves in a horizontal circle of radius r at contact s...
Text Solution
|
- For a particle moving in a horizontal circle with constant angular vel...
Text Solution
|
- In a system of particles, internal forces can change:
Text Solution
|
- Three particles each of mass m are located at the vertices of an equil...
Text Solution
|
- A ball kept in a closed box moves in the box making collisions with th...
Text Solution
|
- A strip of wood of length l is placed on a smooth horizontal surface. ...
Text Solution
|
- The centre of mass of a system of particle is at the origin the number...
Text Solution
|
- Six steel balls of identical size are lined up along a straight frict...
Text Solution
|
- n balls each of mass m impinge elastically each second on a surface wi...
Text Solution
|
- The bob A of a pendulum released from a height h hits head-on another ...
Text Solution
|
- A nucleus moving with velocity bar(v) emits an alpha-particle. Let the...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform sphere is placed on a smooth horizontal surface and a horizo...
Text Solution
|
- Five identical balls each of mass m and radius r are string like beads...
Text Solution
|
- The end of a chain of length L and mass per unit length rho, which is ...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is correct about principle of conservation of m...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod AB of mass m and length l is at rest on a smooth horizon...
Text Solution
|
- A body is fired from point P and strikes at Q inside a smooth circular...
Text Solution
|
- A fixed U-shaped smooth wire has a semi-circular bending between A and...
Text Solution
|
- A collision occurs between two identical balls each of mass m, moving ...
Text Solution
|