A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
LINEAR MOMENTUM & ITS CONSERVATION
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA|Exercise Advance McQ|20 VideosLINEAR MOMENTUM & ITS CONSERVATION
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA|Exercise unsolved|110 VideosLINEAR MOMENTUM & ITS CONSERVATION
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA|Exercise Conceptual MCQ s single option correct|30 VideosKINEMATICS
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA|Exercise Unsolved Numerical Pro.|83 VideosNEWTONS LAWS OF MOTION
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA|Exercise Unsolved Numerical Problem|81 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA-LINEAR MOMENTUM & ITS CONSERVATION-Numerical MCQ s
- A blacksmith carries a hammer on his shoulder and holds in at the othe...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass m moving with a velocity v undergoes an oblique elastic...
Text Solution
|
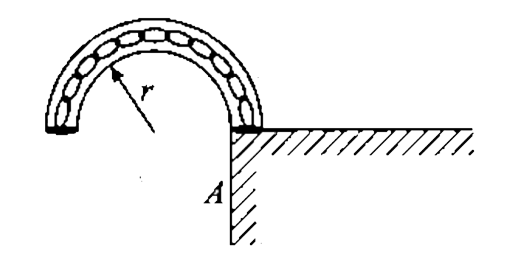
- A smooth semicircular tube AB of radius r is fixed in a vertical plane...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass m moving horizontally at a speed v collides with the bo...
Text Solution
|
- If a man of ,mass M jumps to the ground from a height h and his centr...
Text Solution
|
- A radioactive nucleus of mass number A, initially at rest, emits an al...
Text Solution
|
- A cart of mass M is tied to one end of a massless rope of length 10 m....
Text Solution
|
- A bomb at rest explodes into three fragments of equal massses Two frag...
Text Solution
|
- Four particles of masses m,m 2 m and 2m are placed at the four corner ...
Text Solution
|
- A small coin is placed at a distance r from the centre of a gramophone...
Text Solution
|
- Sphere A of mass 'm' moving with a constant velocity u hits another st...
Text Solution
|
- A smooth sphere is moving on a horizontal surface with velocity vecto...
Text Solution
|
- From a point on smooth floor of a room a toy ball is shot to hit a wal...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown, the heacvy ball of mass 2m rests on the horizon...
Text Solution
|
- A shell is fired from a connot with a velocity V at an angle 0 with th...
Text Solution
|
- A bullet moving with a velcity u passes through a plank which is free ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m(1) makes an elastic one dimensional collision wit...
Text Solution
|
- Two balls with masses in the ratio of 1:2 moving in opposite direction...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical balls of equal masses A and B , are lying on a smooth su...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of mass m(1)"and"m(2) are connected by light inextensible s...
Text Solution
|