Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
SL ARORA-ROTATIONAL MOTION-Problem
- An isolated particle of mass m is moving in a horizontal plane (x-y), ...
Text Solution
|
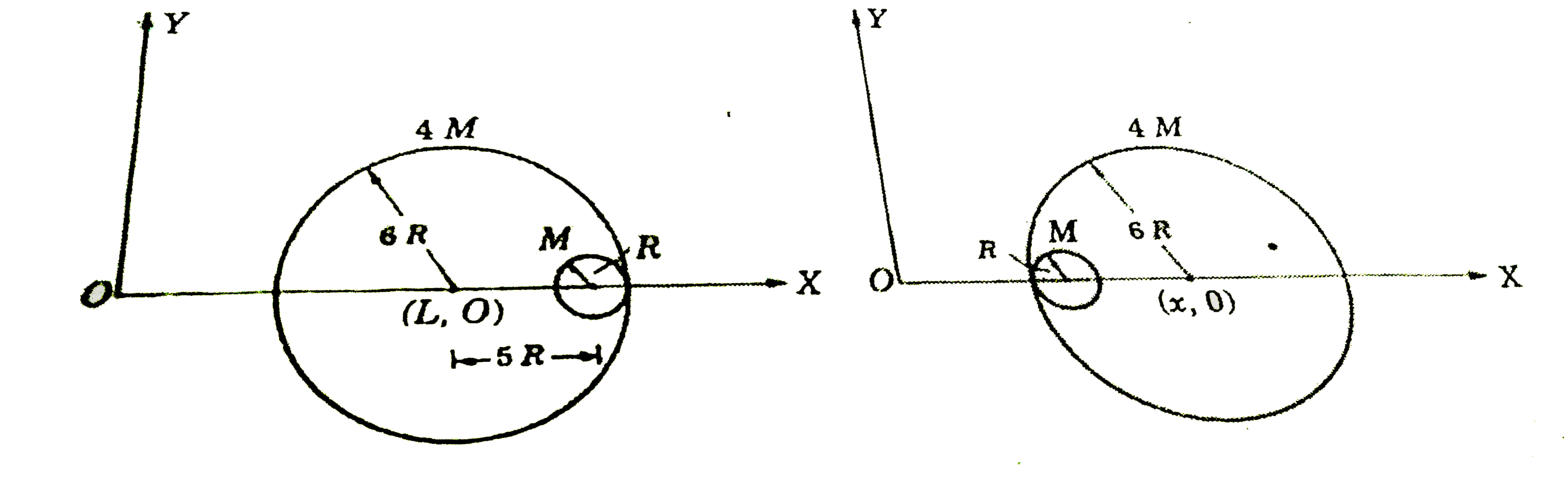
- A small sphere of radius R is held against the inner surface of alpha ...
Text Solution
|
- A boat of 90 kg is floating in still water. A boy of mass 30 kg walks ...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass M with a semicircualr of radius R, rests on a horizont...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of mass m(1) and m(2) are connected to the ends of a spring...
Text Solution
|
- From a uniform circular disc of diameter D, a circular disc or hole of...
Text Solution
|
- Find the coordination of the centre of mass of a uniform semicircular ...
Text Solution
|
- Determine the centre of mass of a uniform hemisphere of radius R.
Text Solution
|
- Determine the position of the centre of mass of a hemisphere of radius...
Text Solution
|
- Determine the coordinate of the centre of mass of a right circular sol...
Text Solution
|
- The driver of a car travelling at speed v suddenly sees a wall at a di...
Text Solution
|
- A very small particle rests on the top of a hemisphere of radius 20 cm...
Text Solution
|
- A tube of length L is filled completely with an incompressible liquid ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle describes a horizontal circle on the smooth surface of an i...
Text Solution
|
- A small block of mass m slides along a smooth track, as shown in fig. ...
Text Solution
|
- Point masses m(1) and m(2) are placed at the ends of a rigid rod of le...
Text Solution
|
- A thin uniform bar lies on a frictionless horizontal surface and is fr...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform bar of length 6a and mass 8 m lies on a smooth horizontal ta...
Text Solution
|
- A homogeneous rod AB of length L = 1.8 m and mass M is pivoted at the ...
Text Solution
|
- A solid cylinder at rest at top of an inclined plane of height 2.7 m r...
Text Solution
|