Topper's Solved these Questions
GRAVITATION
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA|Exercise Particle Exercise|50 VideosGRAVITATION
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA|Exercise Discussion Qns|31 VideosFLUID MECHANICS
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA|Exercise Unsolved Numerical Problems|86 VideosKINEMATICS
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA|Exercise Unsolved Numerical Pro.|83 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA-GRAVITATION-Unsolved Numerical
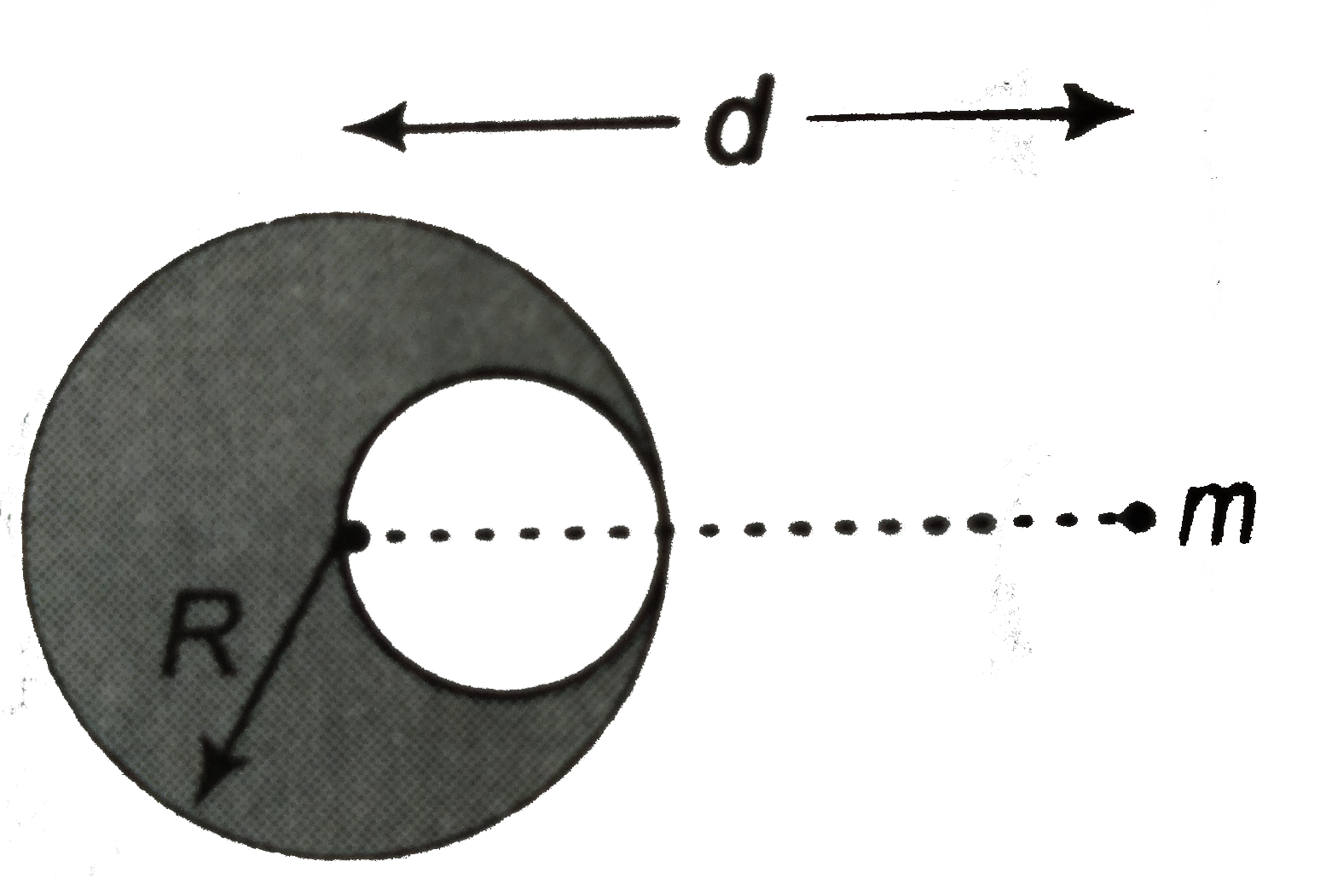
- Figure shows a spherical cavity inside a lead sphere. The surface of t...
Text Solution
|
- At what distance from the center of the earth will a 1 kg object have ...
Text Solution
|
- The radius of Mars is 3.4 xx 10^(6)m and the accelerationof a freely f...
Text Solution
|
- Suppose we invent a unit of mass which we shall call the caendish (C)....
Text Solution
|
- Determine the fractional reduction of the acceleration of gravity due ...
Text Solution
|
- In figure-6.105, particle A has a mass of 1.4 and particle B has a mas...
Text Solution
|
- While investigating the planet Norc in another solar system, we find t...
Text Solution
|
- Two concentric shells of mass m(1) and m(2) are situated as shown. Fin...
Text Solution
|
- Two point masses, each equal to M, are placed a distance 2a apart. Sho...
Text Solution
|
- Computer the mass and density of the moon if acceleration due to gravi...
Text Solution
|
- Two masses m(1) and m(2) at an infinite distance from each other are i...
Text Solution
|
- Imagine a planet whose diameter and mass are both one half of those of...
Text Solution
|
- A thin rod of mass M and length L is bent in a semicircle as shown in ...
Text Solution
|
- Three identical particles each of mass "m" are arranged at the corner...
Text Solution
|
- A smooth tunnel is dug along the radius of earth that ends at centre. ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m is subjected to an attractive central force of ma...
Text Solution
|
- If the radius of the earth were to shrink by one percent its mass rema...
Text Solution
|
- In a certain region of space gravitational field is given by I = - (k/...
Text Solution
|
- A short , straight and frictinless tunnel is bored through the centr...
Text Solution
|
- An iron ball o fradius 1 m and density 8000 kg m^(-3) is placed in ...
Text Solution
|
- Two satellites A and B of equal mass move in the equatorial plane of t...
Text Solution
|