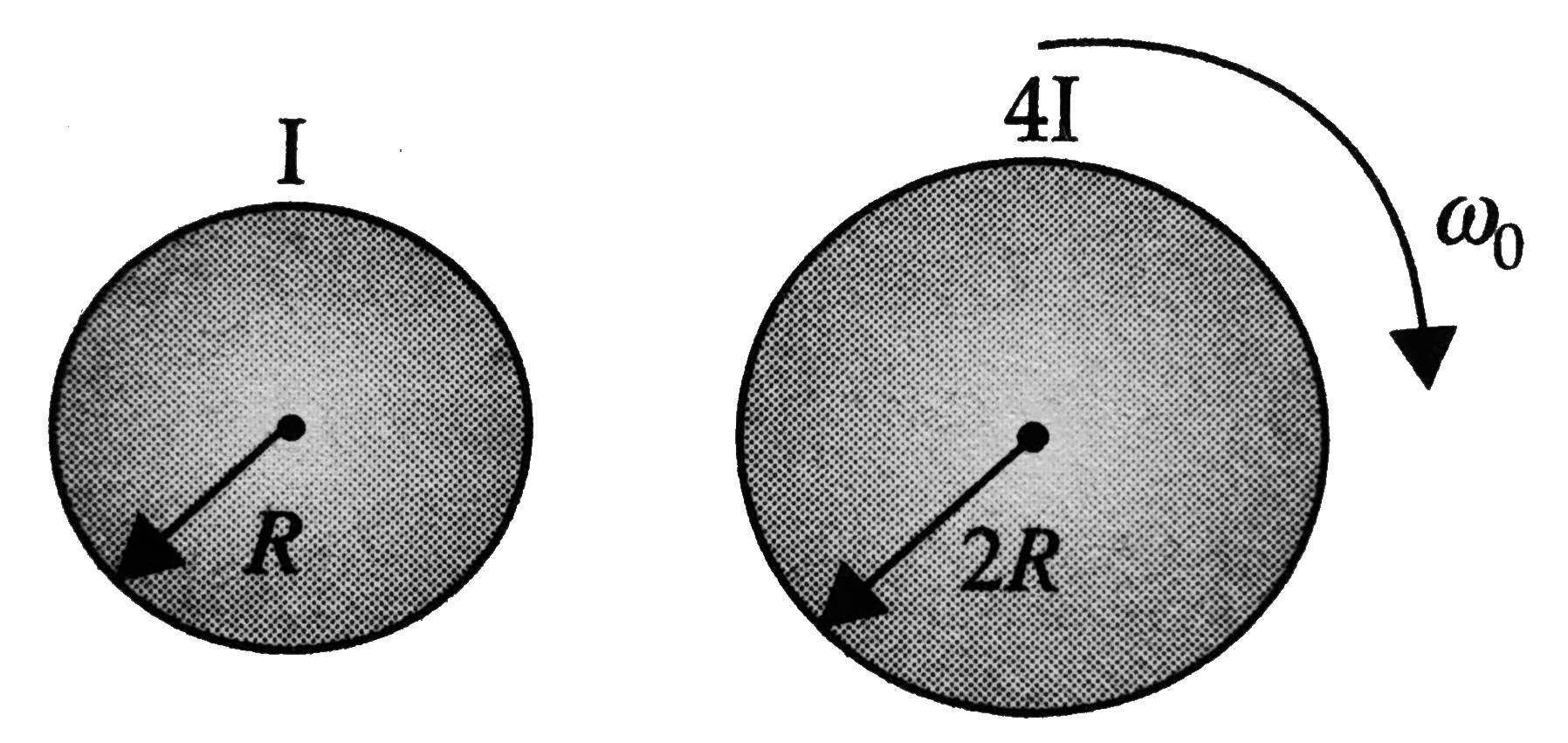
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ROTATIONAL MOTION
DC PANDEY|Exercise A Only One Option is Correct|86 VideosROTATIONAL MOTION
DC PANDEY|Exercise More than one option is correct|36 VideosROTATIONAL MECHANICS
DC PANDEY|Exercise Subjective Questions|2 VideosSEMICONDUCTORS AND ELECTRONIC DEVICES
DC PANDEY|Exercise More than One Option is Correct|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY-ROTATIONAL MOTION-Integer Type Questions
- Two cylinders having radii 2R and R and moment of inertia 4I and I abo...
Text Solution
|
- A ring and a disc having the same mass, roll without slipping with the...
Text Solution
|
- A wheel starting from rest is uniformly acceleration with angular acce...
Text Solution
|
- Radius of gyration of a body about an axis at a distance 6 cm from it ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod of mass 2 kg and length 1 m lies on a smooth horizontal ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod of mass m, hinged at its upper end, is released from res...
Text Solution
|
- An uniform spherical shell of mass m and radius R starts from rest wit...
Text Solution
|
- A small pulley of radius 20 cm and moment of inertia 0.32 kg-m^(2) is ...
Text Solution
|
- If a disc of mass m and radius r is reshaped into a ring a radius 2r,t...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of mass 4 kg and radius 6 metre is free to rotate in horizontal...
Text Solution
|
- Find the acceleration of slid right circular roller A, weighing 12kg w...
Text Solution
|
- Two thin planks are moving on a four identical cylinders as shown. The...
Text Solution
|
- A wheel of radius R=1 m rolls on ground with uniform velocity v=2 m/s ...
Text Solution
|
- A cylinder rolls down on an inclined plane of inclination 37^(@) from ...
Text Solution
|
- A car is moving rightward with acceleration a=gsqrt(k)m//s^(2) . Find ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform thin rod has mass m and length l. One end of the rod lies ov...
Text Solution
|
- A wheel of radius R=2m performs pure rolling on a rough horizontal su...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod of length l and mass m is suspended from one end by inex...
Text Solution
|