Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
SL ARORA-THERMODYNAMICS-Exercise
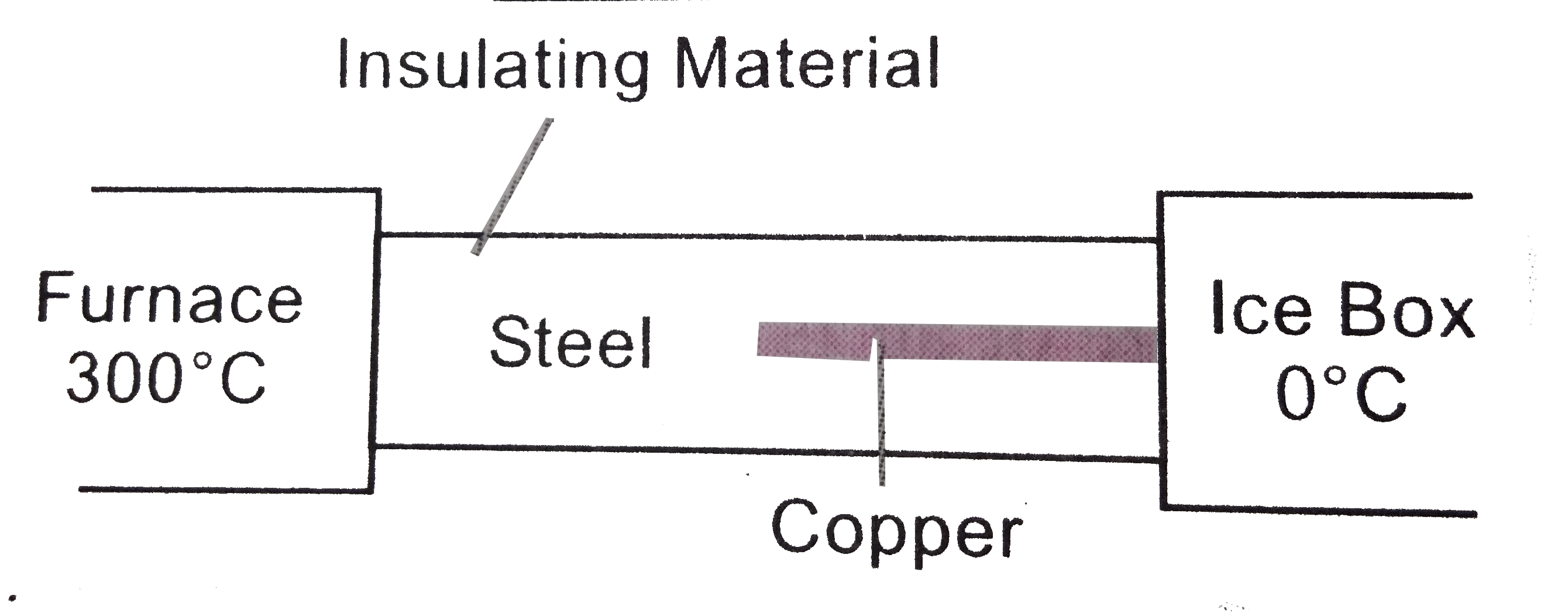
- What is the temperature of the steel-copper junction in the steady sta...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal monoatomic gas is taken around the cycle ABCDA, wher co-ordin...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate net work done by the gas whose thermodynamical behaviour is ...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the change in internal energy of a block of copper of mass 2...
Text Solution
|
- One kg of water at 373K is converted into steam at the same temperatur...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the change in internal energy when 5g of air is heated from ...
Text Solution
|
- A volume of 10m^(3) of a liquid is supplied with 100 kal of heat and e...
Text Solution
|
- The internal energy of a monatomic ideal gas is 1.5 nRT.One mole of he...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the difference between two specific heats of 1 g of nitrogen...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the gas constant for 1 g of gas from the following data : ...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate difference in specific heats for 1 gram of air at N.T.P. Giv...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the ratio of specific heats for nitrogen. Given that the spe...
Text Solution
|
- For hydrogen gas, Cp= 3.409 cal g^-1 ^circC^-1, CV=2.409 cal g^-1 ^cir...
Text Solution
|
- The specific heat of argon at constant pressure is 0.127 and ratio of ...
Text Solution
|
- Two moles of oxygen is heated at a constant pressure from 0^(@)C. What...
Text Solution
|
- A certain gas at atmospheric pressure is compressed adiabatically so t...
Text Solution
|
- A gas is suddenly compressed to 1/4th of its original volume. Caculate...
Text Solution
|
- A tyre pumped to a pressure of 6 atmosphere, suddenly bursts. Room tem...
Text Solution
|
- 200 cm^(3) of a gas is compressed to 100cm^(3) at atmospheric pressure...
Text Solution
|
- A quantity of air at 27^(@)C and atmospheric pressure is suddenly comp...
Text Solution
|
- A quantity of air at normal temperature is compressed (a) slowly (b) s...
Text Solution
|