A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MARVEL PUBLICATION-ROTATIONAL MOTION-TEST YOUR GRASP - 3
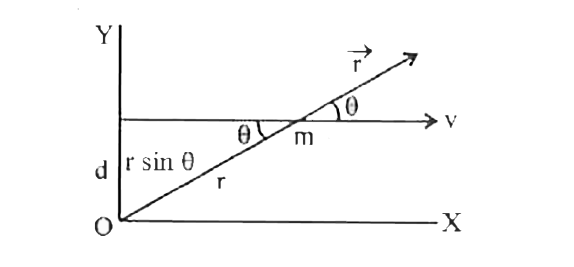
- A particle is moving in the xy-plane with a constant velocity along a ...
Text Solution
|
- A flywheel of mass 4 kg has a radius of gyration of 0.1 m . If it make...
Text Solution
|
- A body of moment of inertia of 3kgm^(2) rotating with an angular veloc...
Text Solution
|
- Three point masses m(1), m(2) and m(3) are located at the vertices of ...
Text Solution
|
- A wheel initially at rest, is rotated with a uniform angular accelerat...
Text Solution
|
- A thin rod of mass m and length 2L is made to rotate about an axis pas...
Text Solution
|
- An iron rod of mass M and length L is cut into n equal parts by cuttin...
Text Solution
|
- About which axis would the moment of inertia of a body be minimum ?
Text Solution
|
- If I is the moment of Inertia and E is the kinetic energy of rotation ...
Text Solution
|