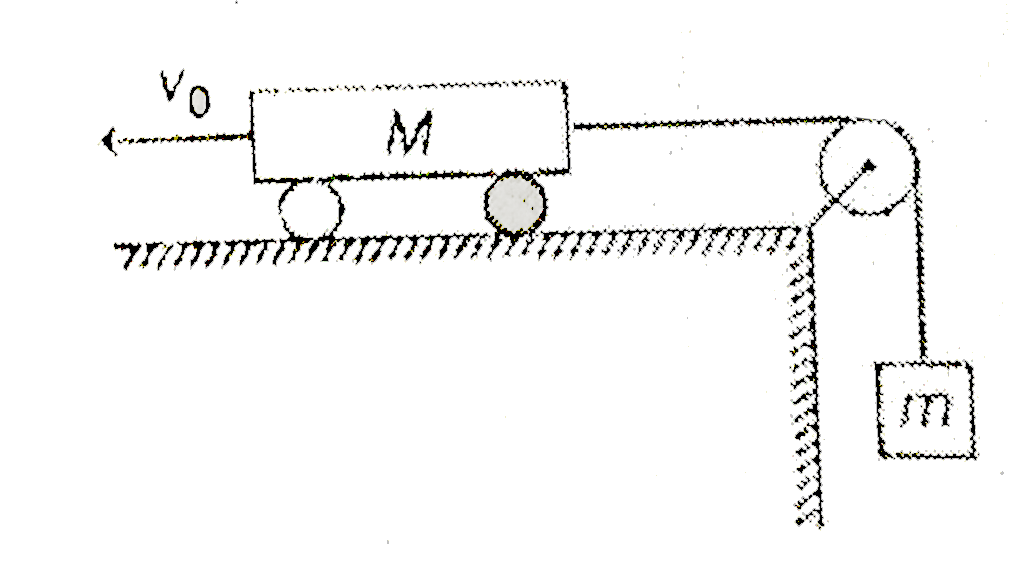
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A cart with a mass M=(1)/(2) kg is connected by a string to a mass of ...
Text Solution
|
- A cart of mass 0.5kg is placed on a smooth surface and is connected by...
Text Solution
|
- Two carts of masses 200 kg and 300 kg on horizontal rails are pushed a...
Text Solution
|
- A cart with a mass M=(1)/(2) kg is connected by a string to a mass of ...
Text Solution
|
- A man of mass 80 kg is riding on a small cart of mass 40 kg which is r...
Text Solution
|
- A cart is moving horizontally along a straight line with constant spee...
Text Solution
|
- A cartis moving horizontally along a straight line with constant speed...
Text Solution
|
- A 3.0-kg cart moving to the right with a speed of 1.0 m/s has a head-o...
Text Solution
|
- A 50.0-kg boy runs at a speed of 10.0 m/s and jumps onto a cart as sho...
Text Solution
|