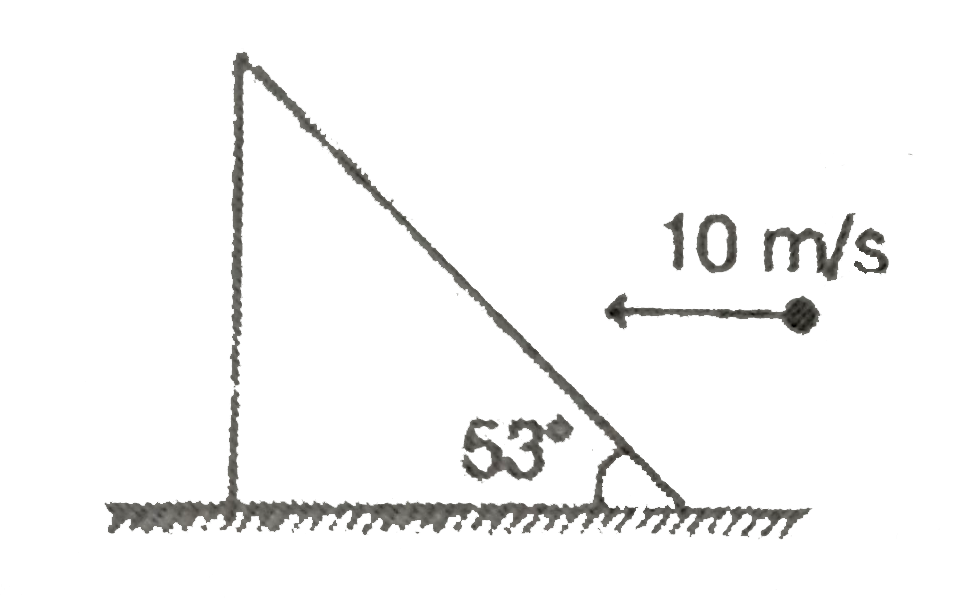
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
CENTRE OF MASS, IMPULSE AND MOMENTUM
DC PANDEY|Exercise Comprehension type questions|15 VideosCENTRE OF MASS, IMPULSE AND MOMENTUM
DC PANDEY|Exercise Only one option is correct for JEE Advanced|55 VideosCENTRE OF MASS
DC PANDEY|Exercise Medical entrances gallery|27 VideosCENTRE OF MASS, LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISION
DC PANDEY|Exercise Level 2 Subjective|21 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems