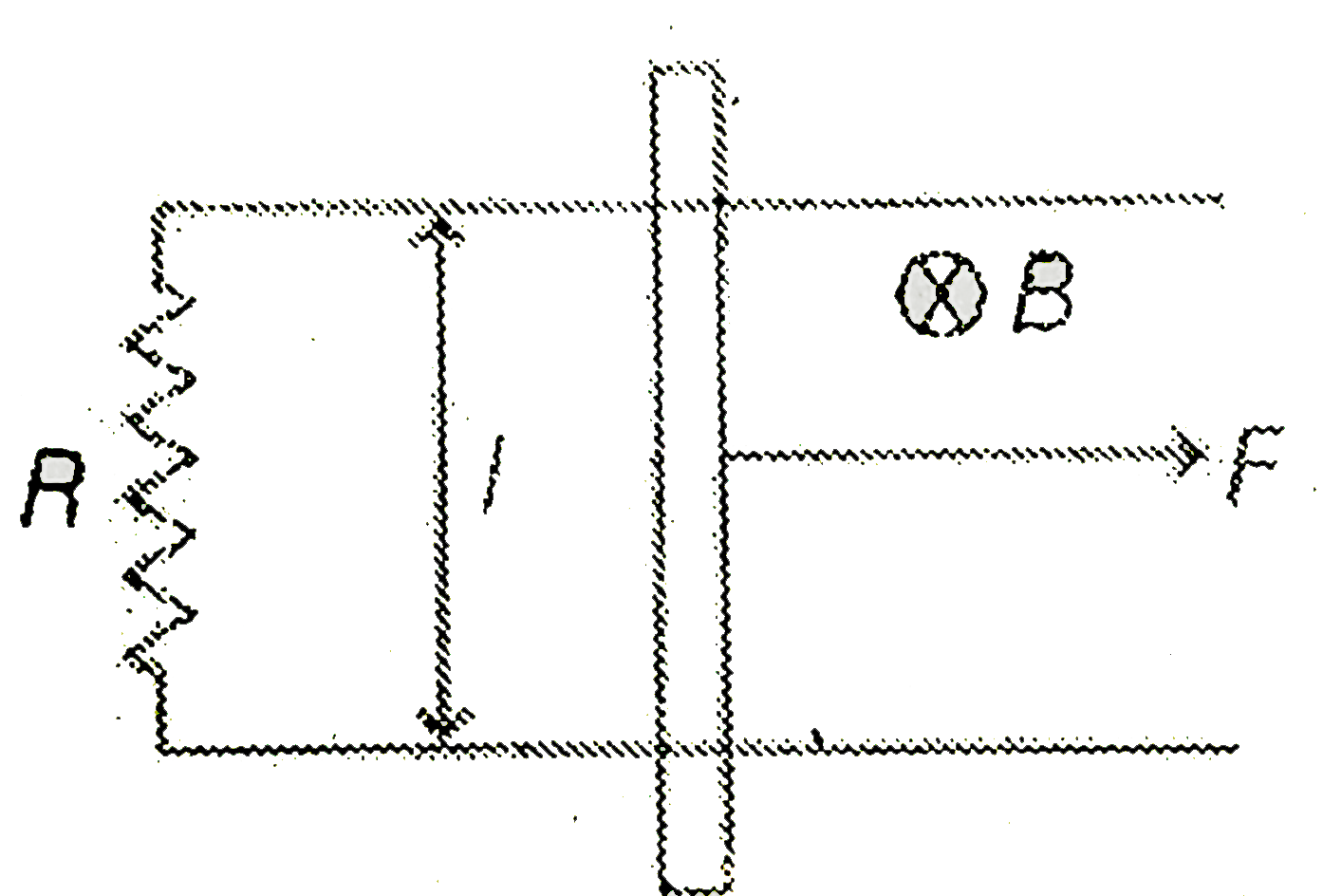
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION AND ALTERNATING CURRENT
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA|Exercise Numerical MCQs|60 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION AND ALTERNATING CURRENT
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA|Exercise Advance MCQs|33 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION AND ALTERNATING CURRENT
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA|Exercise Discussion Question-|21 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA|Exercise All Questions|389 VideosELECTROSTATICS
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA|Exercise Unsolved Numberical Problems|73 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA-ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION AND ALTERNATING CURRENT-Conceptual MCQs
- The area of B-H hysteresis curve is an indication of:
Text Solution
|
- Two identical conducting rings A and B of radius R are rolling over a ...
Text Solution
|
- A constant force is being applied on a road of length 'l' kept at rest...
Text Solution
|
- AB and CD are fixed conducting smooth rails placed in a vertical plane...
Text Solution
|
- An alternating current I in an inductance coil varies with time t acco...
Text Solution
|
- A small circular loop is suspended from an insulating thread. Another ...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown a T-shaped conductor moves with constant angular v...
Text Solution
|
- The permanent magnetic moment of the atoms of a material is not zero. ...
Text Solution
|
- The ring B is coaxial with a solenoid A as shown in figure. As the swi...
Text Solution
|
- Magnetic permeability is maximum for
Text Solution
|
- A conducting rod of length l falls verticaly under gravity in a region...
Text Solution
|
- The figure shows a conducting ring of radius R. A uniform steady magne...
Text Solution
|
- A metallic rod of length l is hinged at the point M and is rotating ab...
Text Solution
|
- At Curie point, a ferromagnetic material transforms into:
Text Solution
|
- A conducting rod is moving with a constant velocity v over the parall...
Text Solution
|
- A rod is rotating with a constant angular velocity omega about point O...
Text Solution
|
- A straight conductig rod PQ is executing SHM in xy-plane from x=-d to ...
Text Solution
|
- A wire is bent in the form of a V shape and placed in a horizontal pl...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown in the figure initialy the switch in position 1 f...
Text Solution
|
- When the switch S is closed at t=0, indentify the correct statement ju...
Text Solution
|