Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
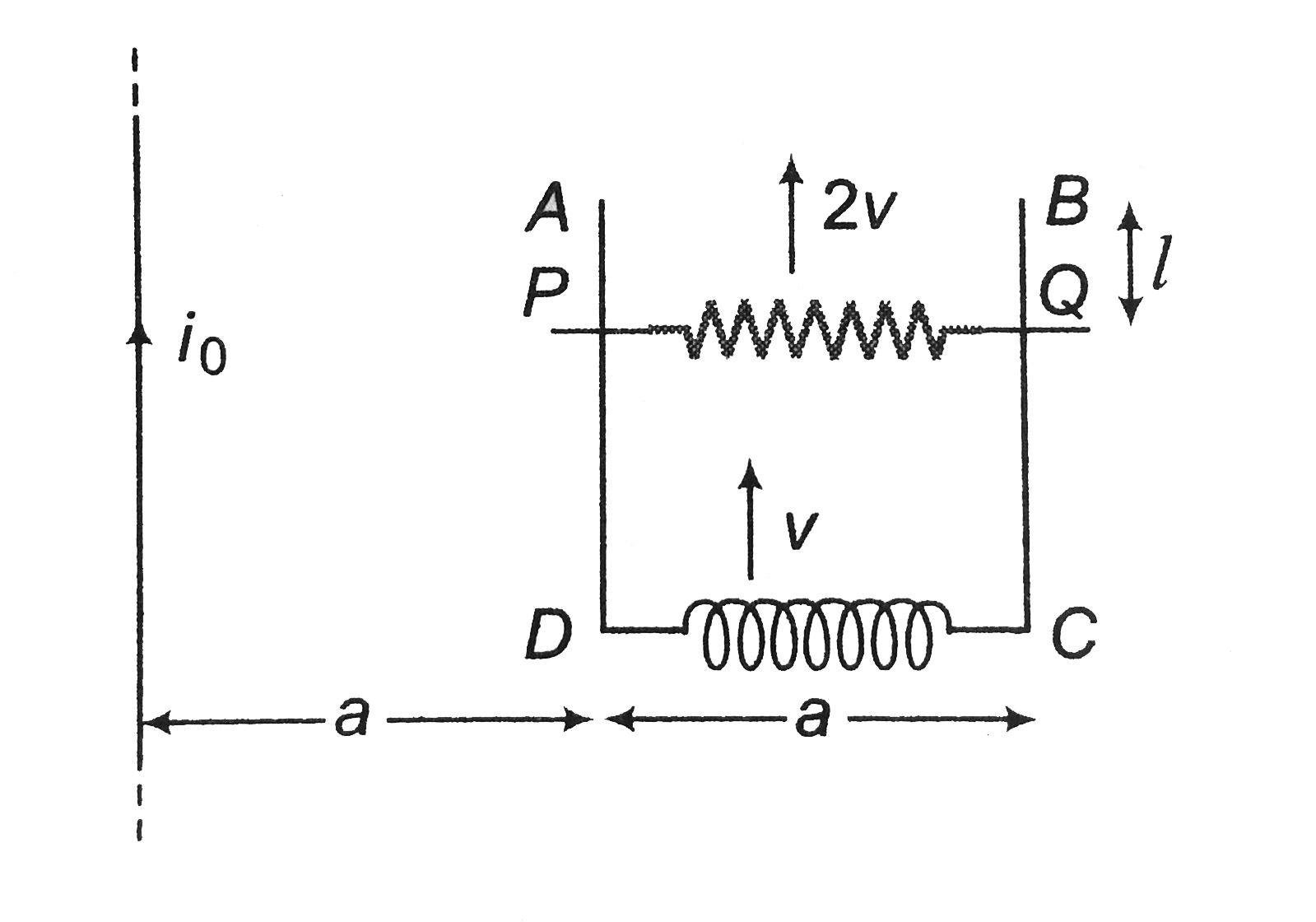
- U-frame ABCD and a sliding rod PQ of resistance R, start moving with v...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting circular loop of radius a and resistance per unit length ...
Text Solution
|
- U-frame ABCD and a sliding rod PQ of resistance R, start moving with v...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of length l is placed perpendicular to a long wire carrying curr...
Text Solution
|
- A metallic rod of mass m and resistance R is sliding over the 2 conduc...
Text Solution
|
- A frame a bed and a sliding rod PQ of resistance R , start moving with...
Text Solution
|
- A long straight wire carries a current I(0), at distance a and b=3a fr...
Text Solution
|
- A long straight wire carries a current I(0). At distance a and b =3a f...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of length l is placed perpendicular to a long wire carrying curr...
Text Solution
|