Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
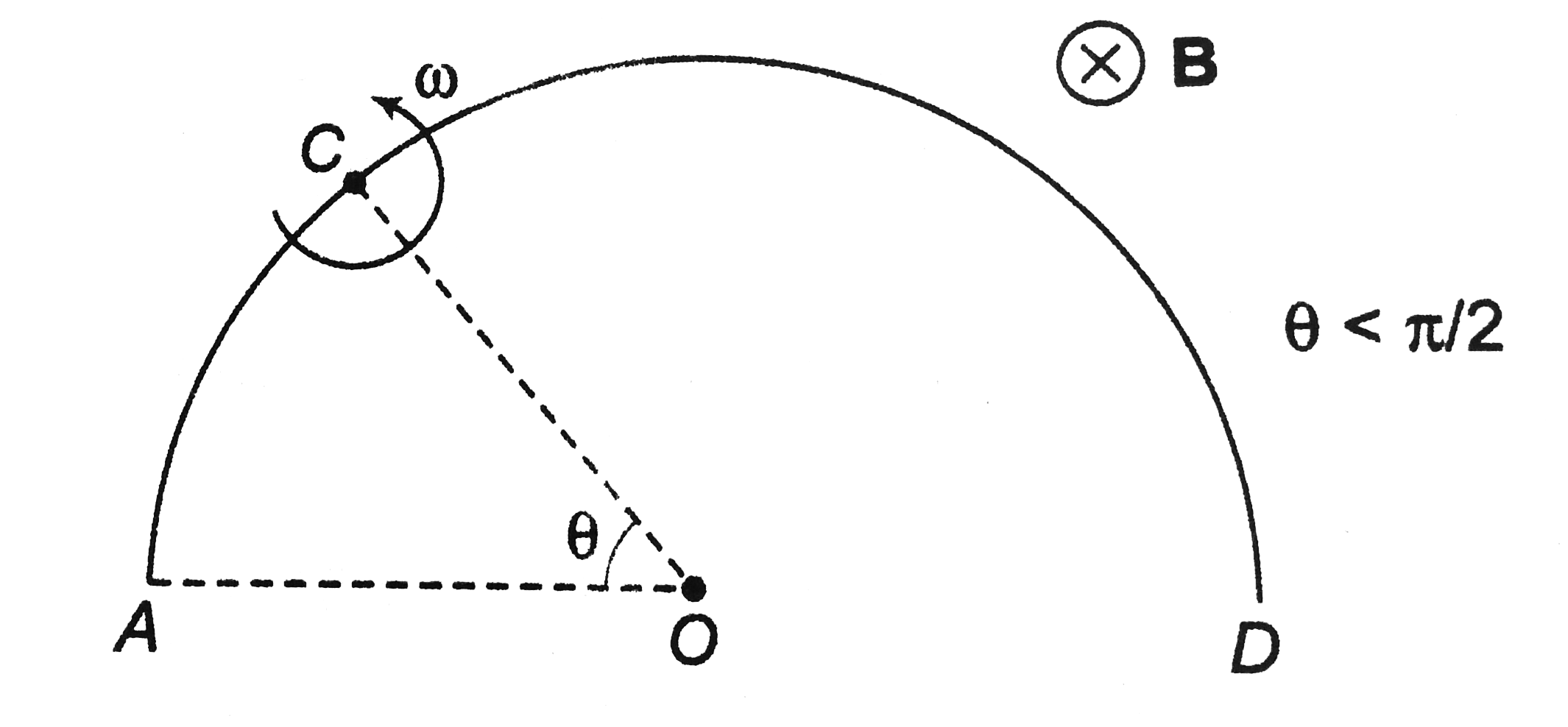
- A uniform wire of resistance per unit length lambda is bent into semi...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of length l rotates with a small but uniform angular velocity om...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of length l rotates with a uniform angular velocity omega about ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform wire of resistance per unit length lambda is bent into semi...
Text Solution
|
- a semicircle wire of radius R is rotated with constant angular velocit...
Text Solution
|
- A wire is bent to form a semi-circle of radius a. The wire rotates abo...
Text Solution
|
- A wire is bent to form a semicircle of the radius a. The wire rotates ...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of length l rotates with a small but uniform angular velocity om...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of length l rotates with a uniform angular velocity omega about ...
Text Solution
|