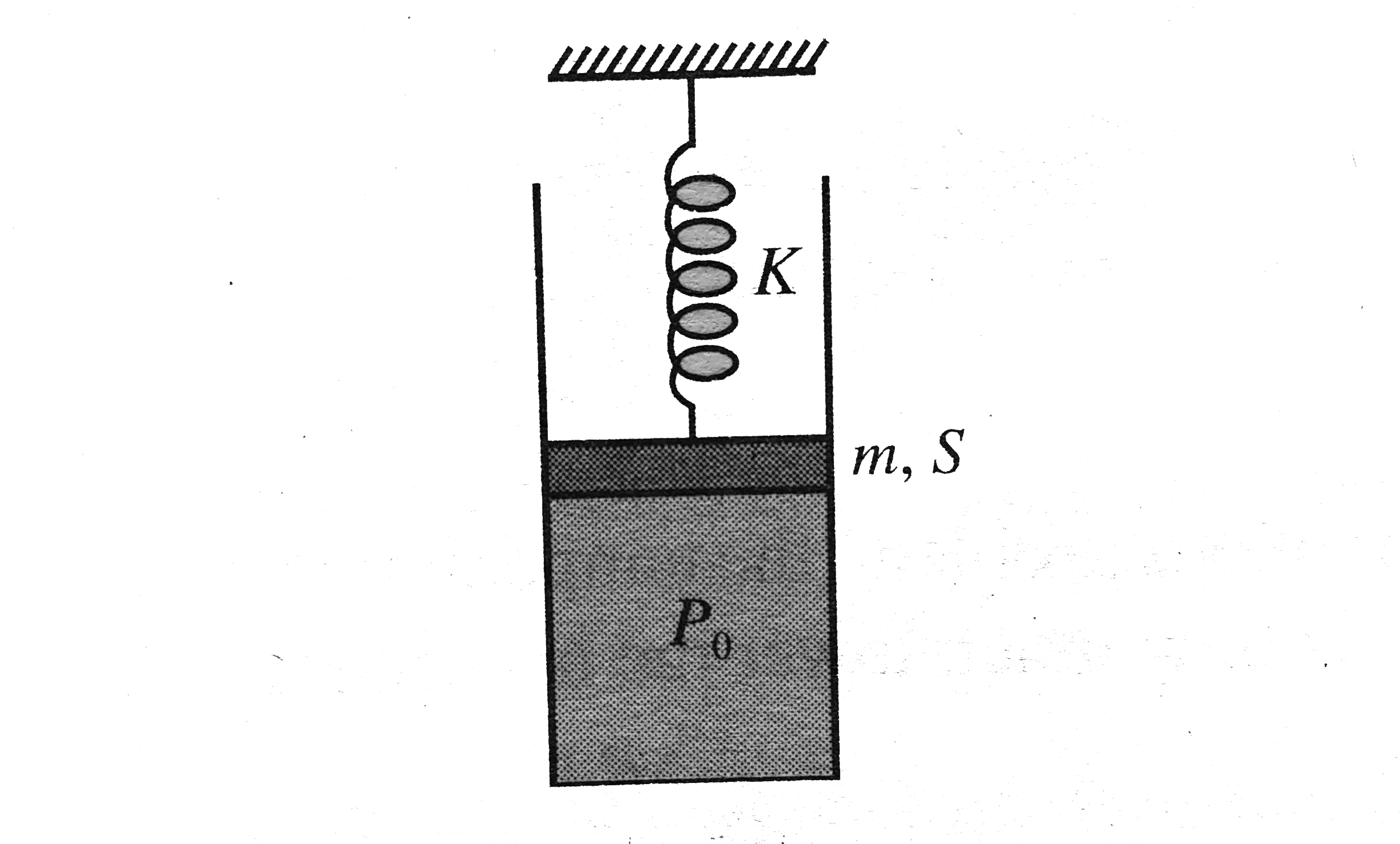
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY-CURRENT ELECTRICITY-All Questions
- Two spheres A and B have radius but the heat capacity of A is greater ...
Text Solution
|
- A thermally insulated chamber of volume 2V(0) is divided by a friction...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement shown in Fig. gas is thermally insulated. An ideal ...
Text Solution
|
- P - V diagram of a cyclic process ABCA is as shown in Fig. Choose the ...
Text Solution
|
- A gas undergoes change in its state from position A to position B via ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the quantity (MkT)/(pV) of an ideal gas where M is the mass o...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following quantities is independent of the nature of the ...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following quantities depend on temperature only for a giv...
Text Solution
|
- During the process AB of an ideal gas
Text Solution
|
- Temperature versus pressure graph of an ideal gas is shown in Fig. Dur...
Text Solution
|
- Internal energy of an ideal diatomic gas at 300 K is 100 J. In this 10...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas is allowed to expand in vacuum in rigid insulator contain...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of an ideal monoatomaic gas is taken from A to C along the pa...
Text Solution
|
- The temperature drop through a two layer furnace wall is 900^@C. Each ...
Text Solution
|
- n moles of a monoatomic gas undergoes a cyclic process ABCDA as shown....
Text Solution
|
- At ordinary temperatures, the molecules of an ideal gas have only tran...
Text Solution
|
- 1 kg of ice at 0^(@)C is mixed with 1.5 kg of water at 45^(@)C [latent...
Text Solution
|
- A vessel contains 1 mole of O(2) gas (molar mass 32) at a temperature ...
Text Solution
|
- In a thermodynamic process helium gas obeys the law TP^(-2//5) = const...
Text Solution
|
- The ednsity (rho) of an ideal gas varies with temperature T as shown i...
Text Solution
|