A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CURRENT ELECTRICITY
DC PANDEY|Exercise Match the columns|4 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
DC PANDEY|Exercise Medical entrances gallery|97 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
DC PANDEY|Exercise Taking it together|142 VideosCOMMUNICATION SYSTEM
DC PANDEY|Exercise Subjective|11 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
DC PANDEY|Exercise Medical entrances gallery|25 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY-CURRENT ELECTRICITY-B. Assertion and reason
- Assertion : V = iR is Ohm's law. Reason : V - I graph is always a st...
Text Solution
|
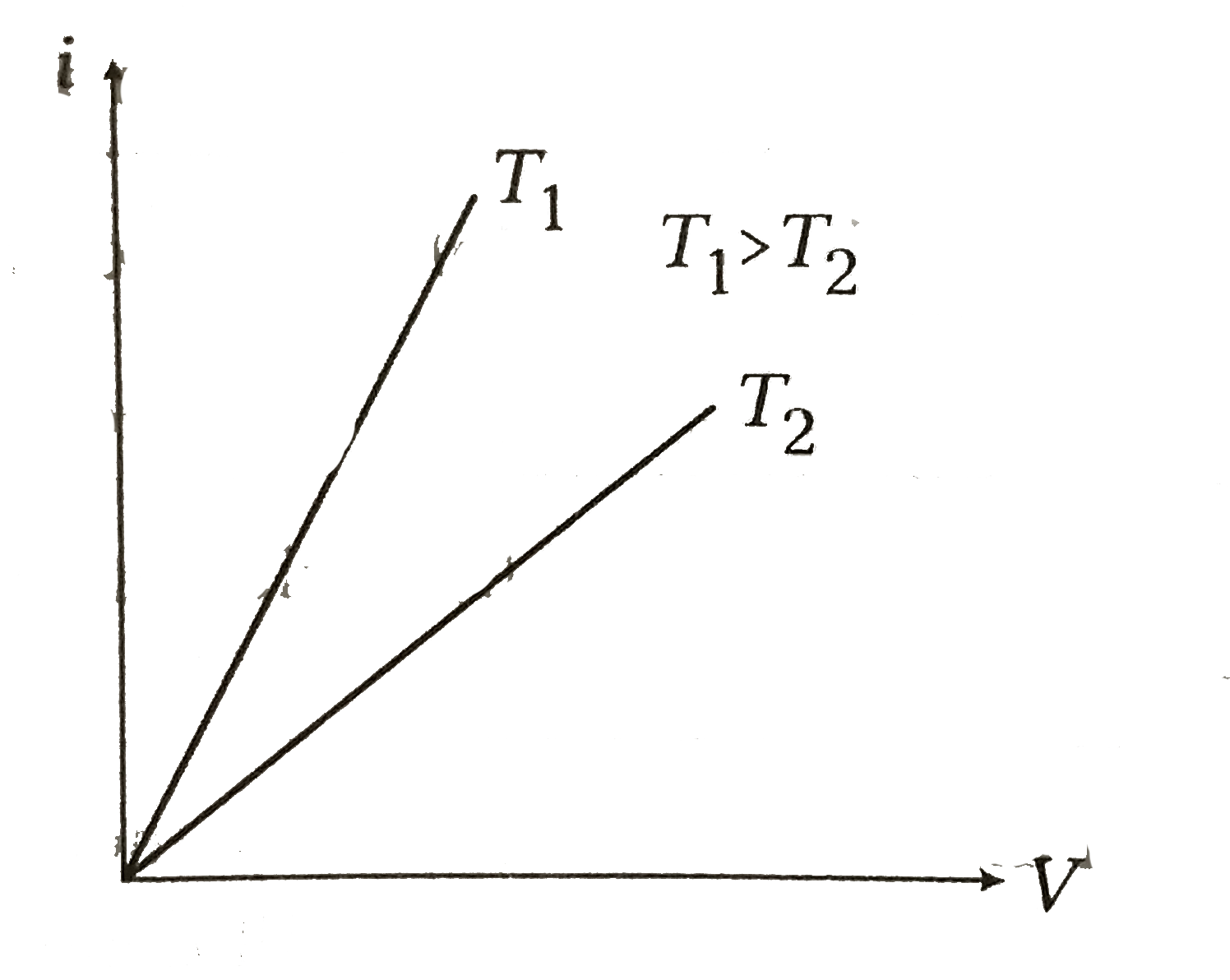
- Assertion : Current versus potential difference (i-V) graph for a cond...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : If a current flows through a wire of non-uniform cross-sec...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : In our houses when we start switching on different light b...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : If a current is flowing through a conducting wire of non-u...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : Kilovol-ampere (kVA) and kilowatt-hour have the same dimen...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : If by mistake, a voltmeter is connected in series, then ci...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : Resistance of an ammeter is less than the resistance of a ...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : A resistance wire is broken into four pices and all are co...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : Potential difference across the terminals of a battery is ...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : Inside a conductor, electrons have no motion in the absenc...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : Current between two points in an electrical always flows f...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : In case of potentiometer experiment, if emfs of known and ...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : In potentiometer experiment, null point cannot be obtained...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : In the circuit shown in figure, battery is ideal. If a res...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : Two 60 W bulbs are first connected in series and then in p...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : Two resistance wires shown in figure are of same material....
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : Two identical bulbs when connected across a battery, produ...
Text Solution
|