Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY-CALORIMETRY AND HEAT TRANSFER-Medical entrance s gallery
- Three bars of equal lengths and equal area of cross-section are connec...
Text Solution
|
- A black body is at a temperature of 5760 K. The energy of radiation em...
Text Solution
|
- A piece of ice falls from a height h so that it melts completely. Only...
Text Solution
|
- The two ends of a metal rod are maintained at temperature 100^(@)C and...
Text Solution
|
- The black body spectrum of an object O(1) is such that its radiant int...
Text Solution
|
- Two plates of same area are placed in contact. Their thickness as well...
Text Solution
|
- If the wavelength corresponding to maximum energy radiated from the mo...
Text Solution
|
- A solid at temperature T(1) is kept in an evacuated chamber at tempera...
Text Solution
|
- A black body with surface area 0.001 m^(2) is heated upto a temperatur...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the meaningless
Text Solution
|
- Water is being boiled in flat bottom kettle placed on a stove. The are...
Text Solution
|
- A cylinder of radius R made of a material of thermal conductivity K1 i...
Text Solution
|
- On observing light from three different stars P, Q and R, it was found...
Text Solution
|
- A piece of ice of mass 100 g and at temperature 0^@ C is put in 200 g ...
Text Solution
|
- A pan filled with hot food cools from 94^(@)C to 86^(@)C in 2 minutes ...
Text Solution
|
- 1 g of ice at 0^@C is mixed with 1 g of steam at 100^@C. After thermal...
Text Solution
|
- Stream at 100^(@)C is passed into 20 g of water at 10^(@)C. When water...
Text Solution
|
- A 10 W electric heater is used to heat a container filled with 0.5 kg ...
Text Solution
|
- A block of ice of mass 50kg is sliding on a horizontal plane. It start...
Text Solution
|
- Same quantity of ice is filled in each of the two metal container P an...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical rods are connected between two containers. One of them i...
Text Solution
|
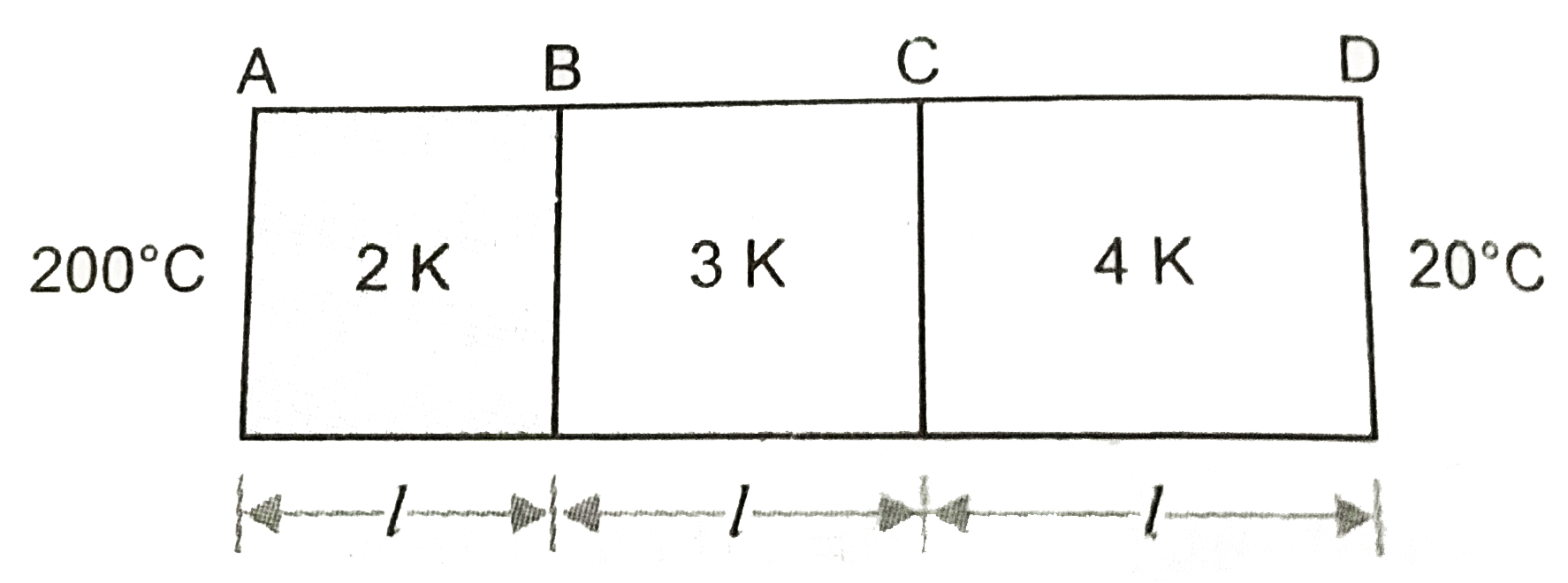 .
.