A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CALORIMETRY AND HEAT TRANSFER
DC PANDEY|Exercise Assertion and reason|17 VideosCALORIMETRY AND HEAT TRANSFER
DC PANDEY|Exercise Match the columns|4 VideosCALORIMETRY AND HEAT TRANSFER
DC PANDEY|Exercise Check points 16.4|25 VideosCALORIMETRY & HEAT TRANSFER
DC PANDEY|Exercise Level 2 Subjective|14 VideosCENTRE OF MASS
DC PANDEY|Exercise Medical entrances gallery|27 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY-CALORIMETRY AND HEAT TRANSFER-Taking it together
- If a body coated black at 600K surrounded by atmosphere at 300 K has c...
Text Solution
|
- The power radiated by a black body is P, and it radiates maximum energ...
Text Solution
|
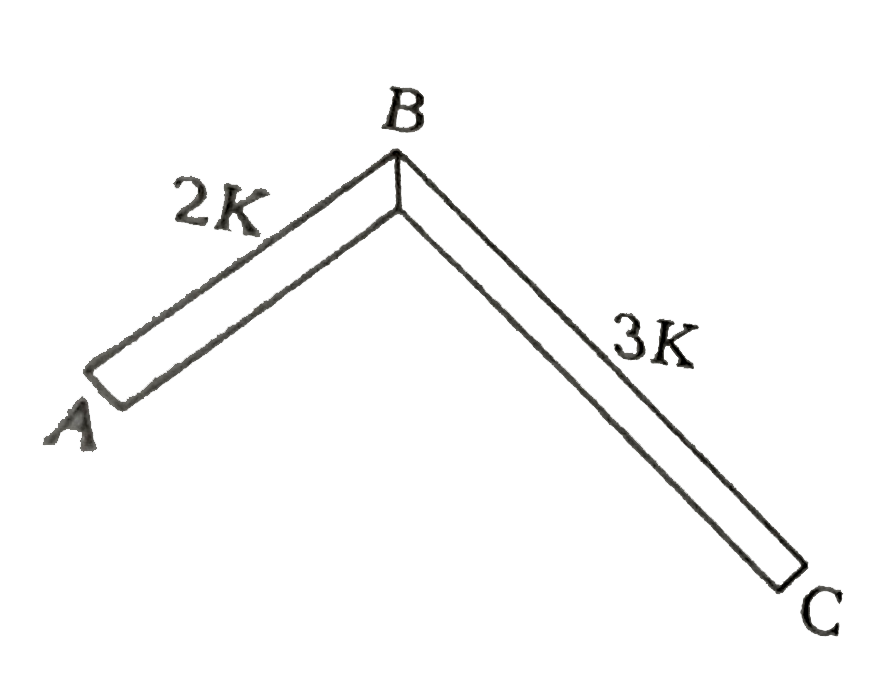
- In the figure ABC is a conducting rod whose lateral surfaces are insul...
Text Solution
|
- Two similar rods are joined as shown in figure. Then temperature of ju...
Text Solution
|
- Five rods of same dimensions are arranged as shown in the figure. They...
Text Solution
|
- Three identical metal rods A, B and C are placed end to end and a temp...
Text Solution
|
- 0.3 Kg of hot coffee, which is at 70^(@)C, is poured into a cup of mas...
Text Solution
|
- A calorimeter contains 10 g of water at 20^(@)C. The temperature falls...
Text Solution
|
- 19 g of water at 30^@C and 5 g of ice at -20^@C are mixed together in ...
Text Solution
|
- Work done in converting 1 g of ice at -10^@C into steam at 100^@C is
Text Solution
|
- Two rigid boxes containing different ideal gases are placed on a table...
Text Solution
|
- The figure given below shows the cooling curve of pure wax material af...
Text Solution
|
- Three conducting rods of same material and cross-section are shown in ...
Text Solution
|
- Two rods with the same dimensions have thermal conductivities in the r...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical conducting rods are first connected independently to two...
Text Solution
|
- Three rods of identical area of cross-section and made from the same m...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical rods are made of different materials whose thermal condu...
Text Solution
|
- The temperature change versus heat supplied curve is given for 1 kg of...
Text Solution
|
- 2kg of ice at 20^@C is mixed with 5kg of water at 20^@C in an insulati...
Text Solution
|
- 10 gm of ice cubes at 0^(@)"C" are released in a tumbler (water equi...
Text Solution
|