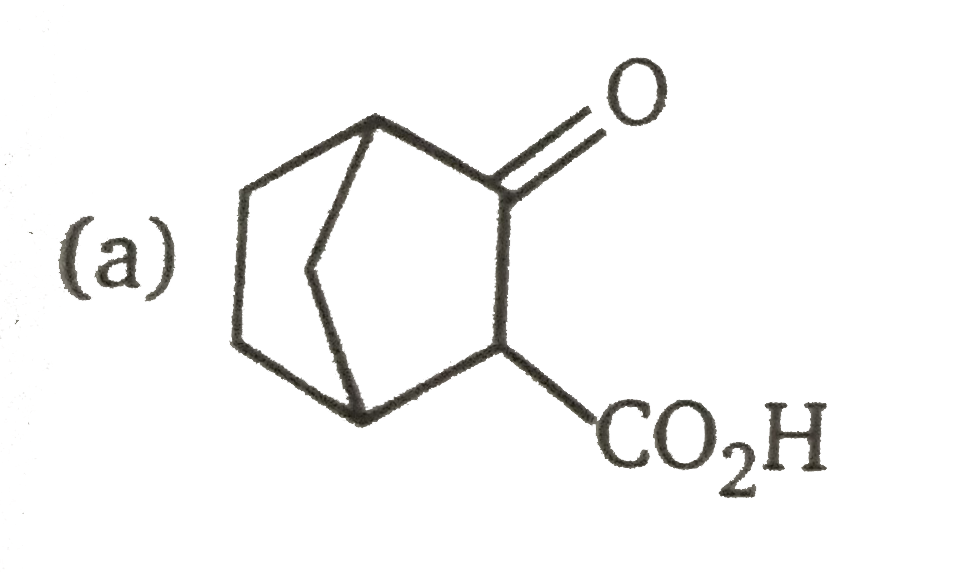
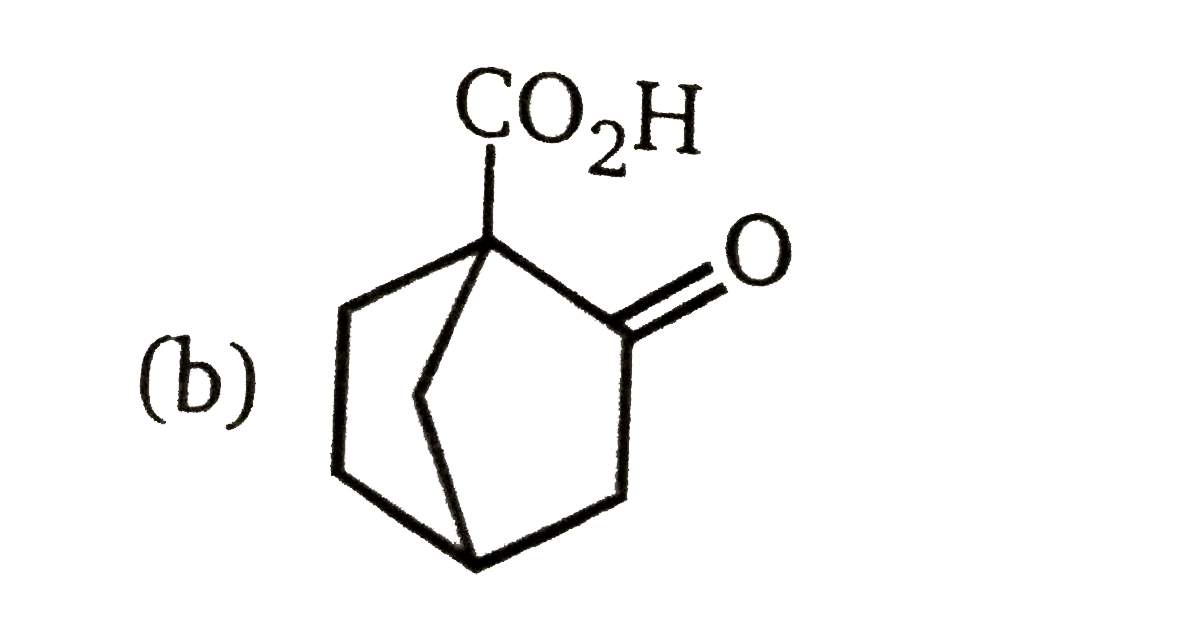
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CARBOXYLIC ACID AND THEIR DERIVATIVES
MS CHOUHAN|Exercise Level 1 (Q.1 To Q.30)|1 VideosCARBOXYLIC ACID AND THEIR DERIVATIVES
MS CHOUHAN|Exercise Level 1 (Q.31 To Q.60)|1 VideosCARBOHYDRATES
MS CHOUHAN|Exercise MULTIPLE CORRECT CHOICE TYPE (INTEGER TYPE)|1 VideosCARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVES
MS CHOUHAN|Exercise ADDITIONAL OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS (Matrix Match Type)|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems