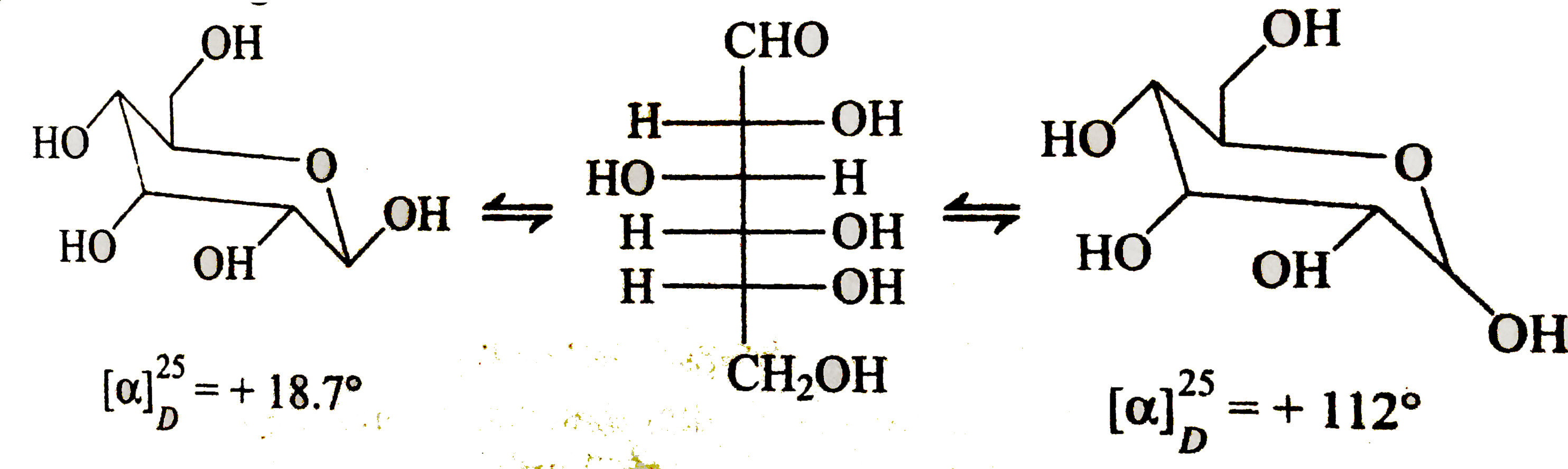A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
BIOMOLECULES
HIMANSHU PANDEY|Exercise Match The Column|6 VideosBIOMOLECULES
HIMANSHU PANDEY|Exercise More Than One Correct|23 VideosAROMATIC HYDROCARBONS
HIMANSHU PANDEY|Exercise Subjective Type Problems|9 VideosCABOXYLIC ACIDS AND ITS DERIVATIVES
HIMANSHU PANDEY|Exercise Subjective Type Problems|8 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
HIMANSHU PANDEY-BIOMOLECULES-Linked Comprehension Type
- The isoelectric point(pl) of an amino acid is the pH of wihc it has no...
Text Solution
|
- The isoelectric point(pl) of an amino acid is the pH of wihc it has no...
Text Solution
|
- The isoelectric point(pl) of an amino acid is the pH of wihc it has no...
Text Solution
|
- Compounds 'X' is :
Text Solution
|
- Compound 'Z' is :
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following are the reducing sugars?
Text Solution
|
- D(+) Glucose has melting point 146^(@)C and specific rotation [alpha](...
Text Solution
|
- D(+) Glucose has melting point 146^(@)C and specific rotation [alpha](...
Text Solution
|
- D(+) Glucose has melting point 146^(@)C and specific rotation [alpha](...
Text Solution
|
- Protein are nitrogeneous organic compound having very high molecular m...
Text Solution
|
- Protein are nitrogeneous organic compound having very high molecular m...
Text Solution
|
- Protein are nitrogeneous organic compound having very high molecular m...
Text Solution
|