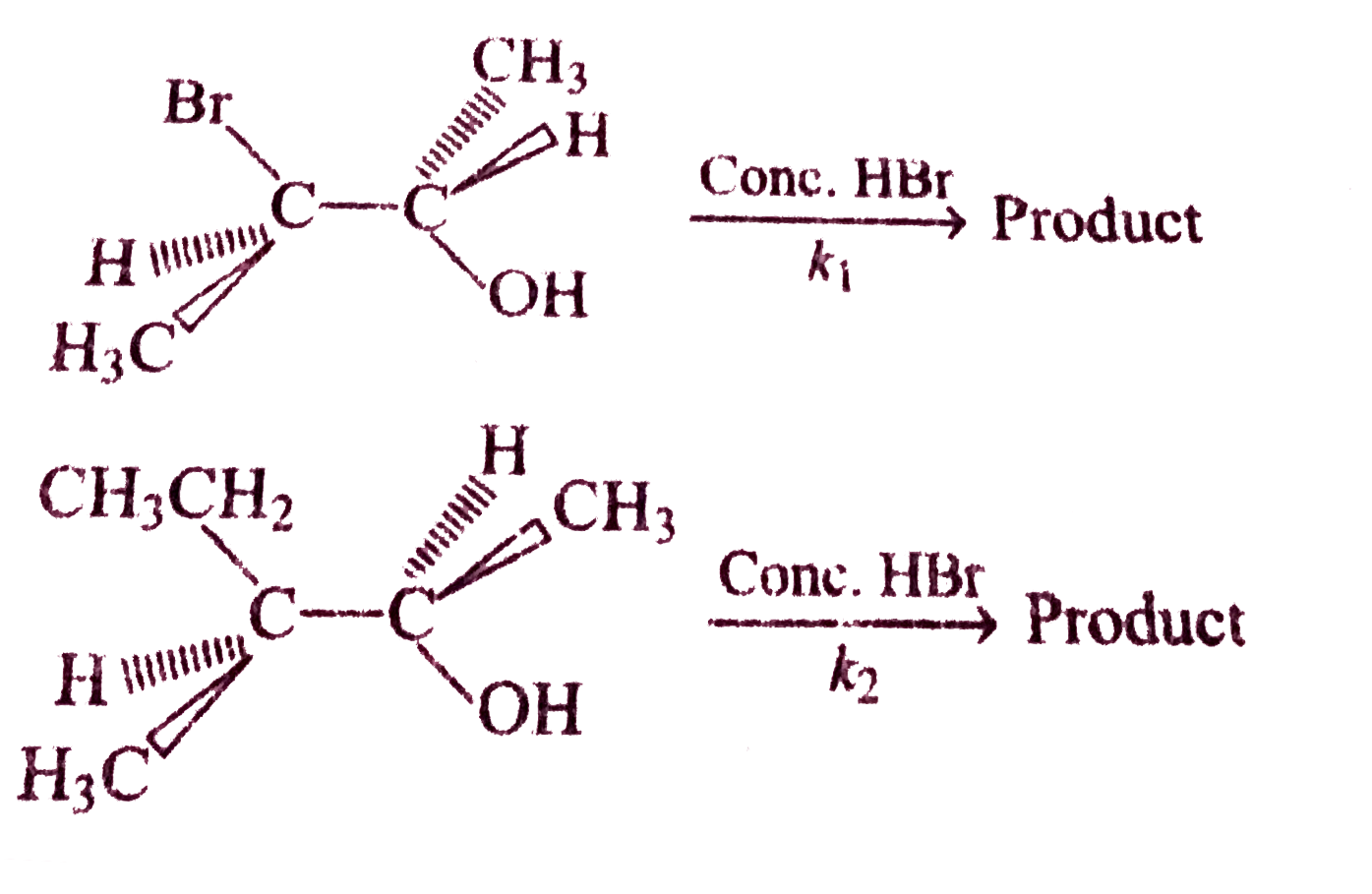
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- -OH group is substituted by -Br. The slowest step is dehydration. Whic...
Text Solution
|
- A reaction takes place in theee steps: the rate constant are k(1), k(2...
Text Solution
|
- A reaction takes place in theee steps: the rate constant are k(1), k(2...
Text Solution
|
- A reaction takes place in three rate determining steps having rate con...
Text Solution
|
- A reaction takes place in three steps. The rate constant are k(1), k(2...
Text Solution
|
- -OH group is substituted by -Br. The slowest step is dehydration. Whic...
Text Solution
|
- -OH group is substituted by -Br. The slowest step is dehydration. Whic...
Text Solution
|
- If K(1)= Rate constant at temperature T(1) and k(2) rate constant at t...
Text Solution
|
- A reaction takes place in three steps with individual rate constant a...
Text Solution
|