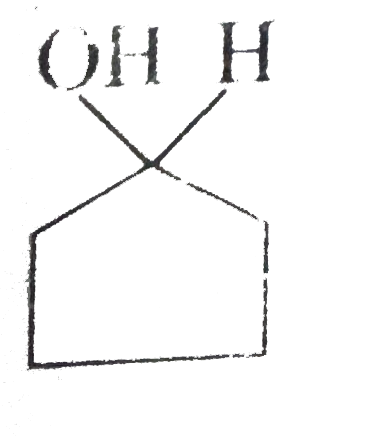
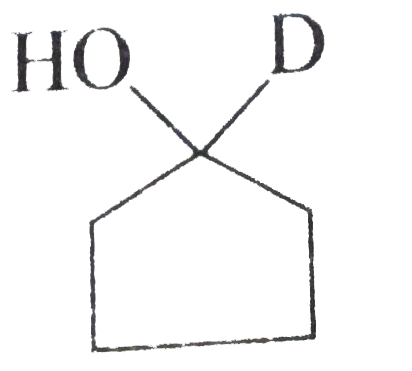
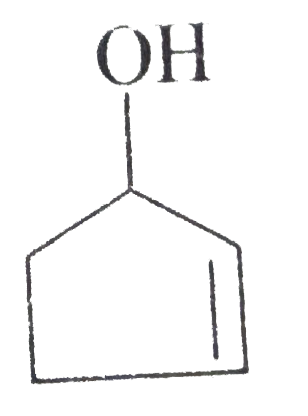
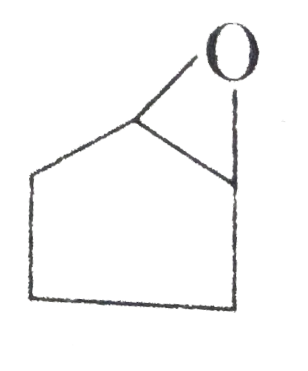
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Carbon oxygen double bond are easily reduced by NaBH(4) or LiAlH(4). T...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is reduced most easily to an alkane by NaBH(4) ...
Text Solution
|
- The maximum number of moles of carbonyl compound (aldehyde or ketone) ...
Text Solution
|
- Match the column {:("Column I","Column II"),("(A) acid chloride","(...
Text Solution
|
- Carbon oxygen double bond are easily reduced by NaBH(4) or LiAlH(4). T...
Text Solution
|
- Carbon oxygen double bond are easily reduced by NaBH(4) or LiAlH(4). T...
Text Solution
|
- Carbon oxygen double bond are easily reduced by NaBH(4) or LiAlH(4). T...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : LiAlH(4) is more reactive and less selctive than NaBH(4) ...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the product? (i). overset(NaBH(4))larrMe-CHOoverset(LiAIH(4...
Text Solution
|
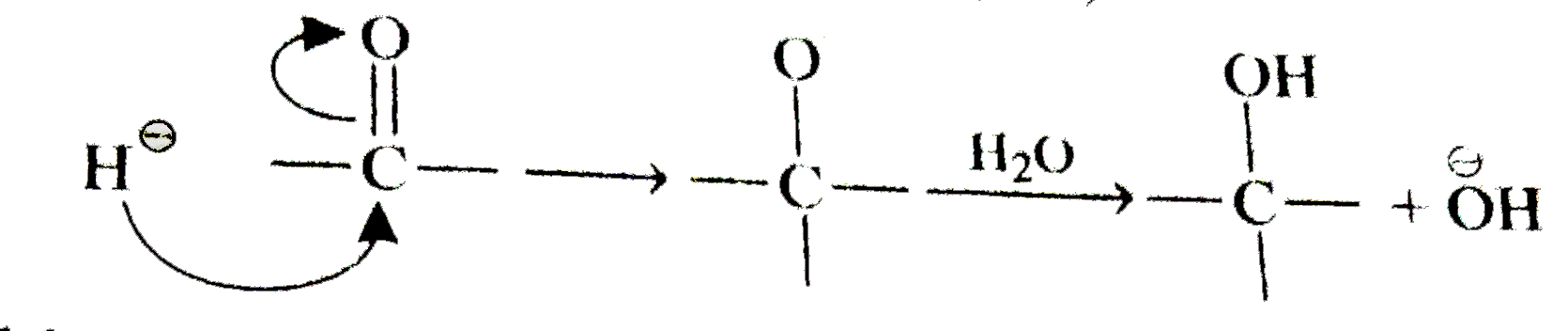
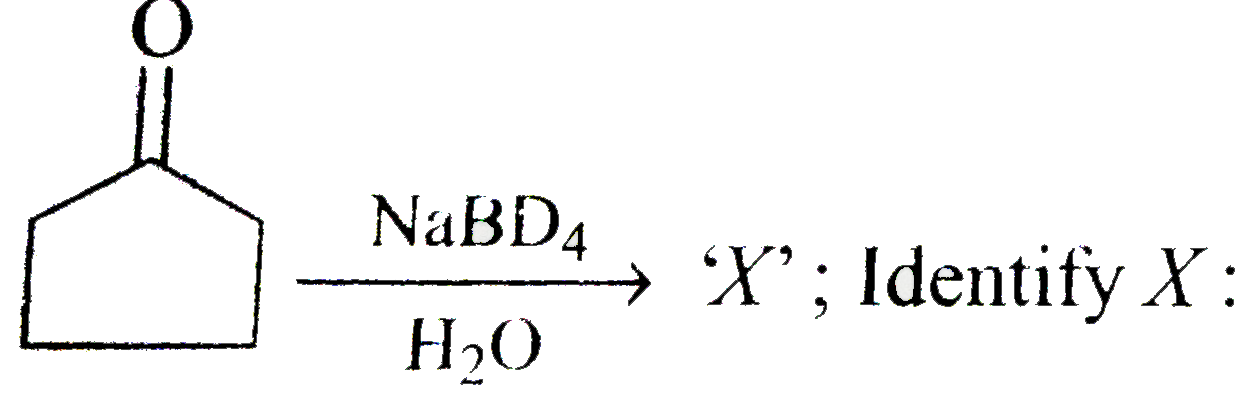 , Identify X:
, Identify X: