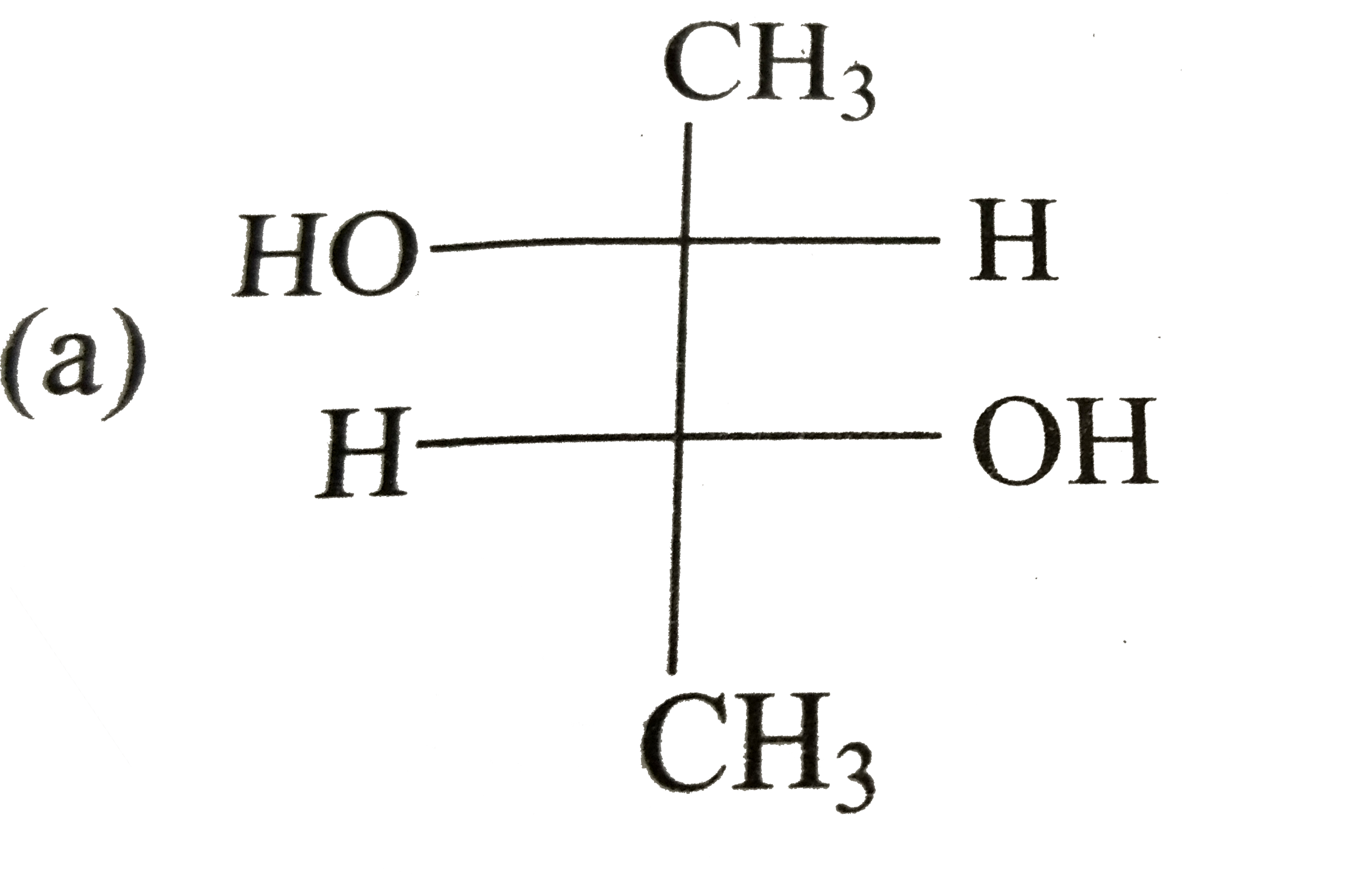
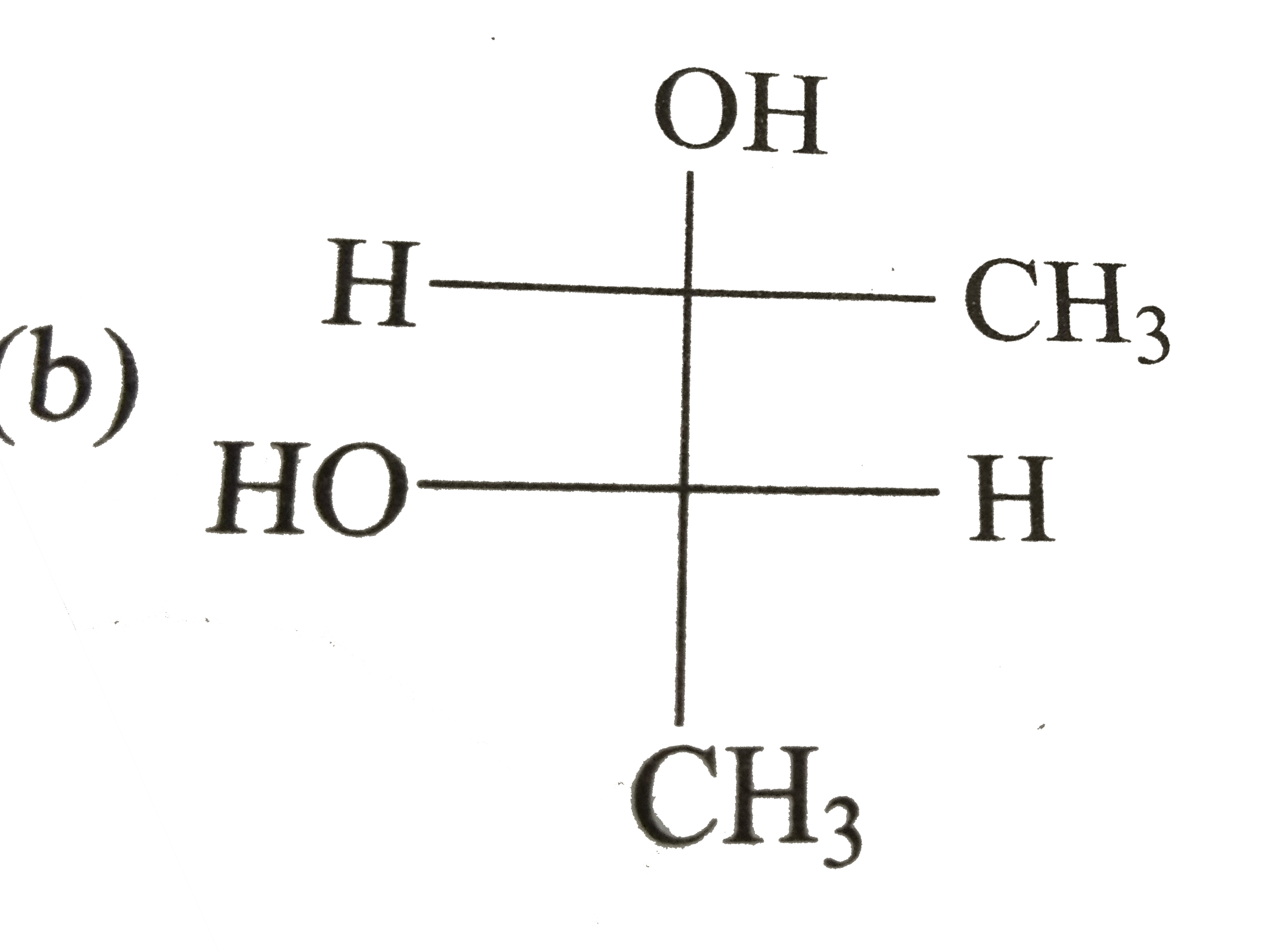
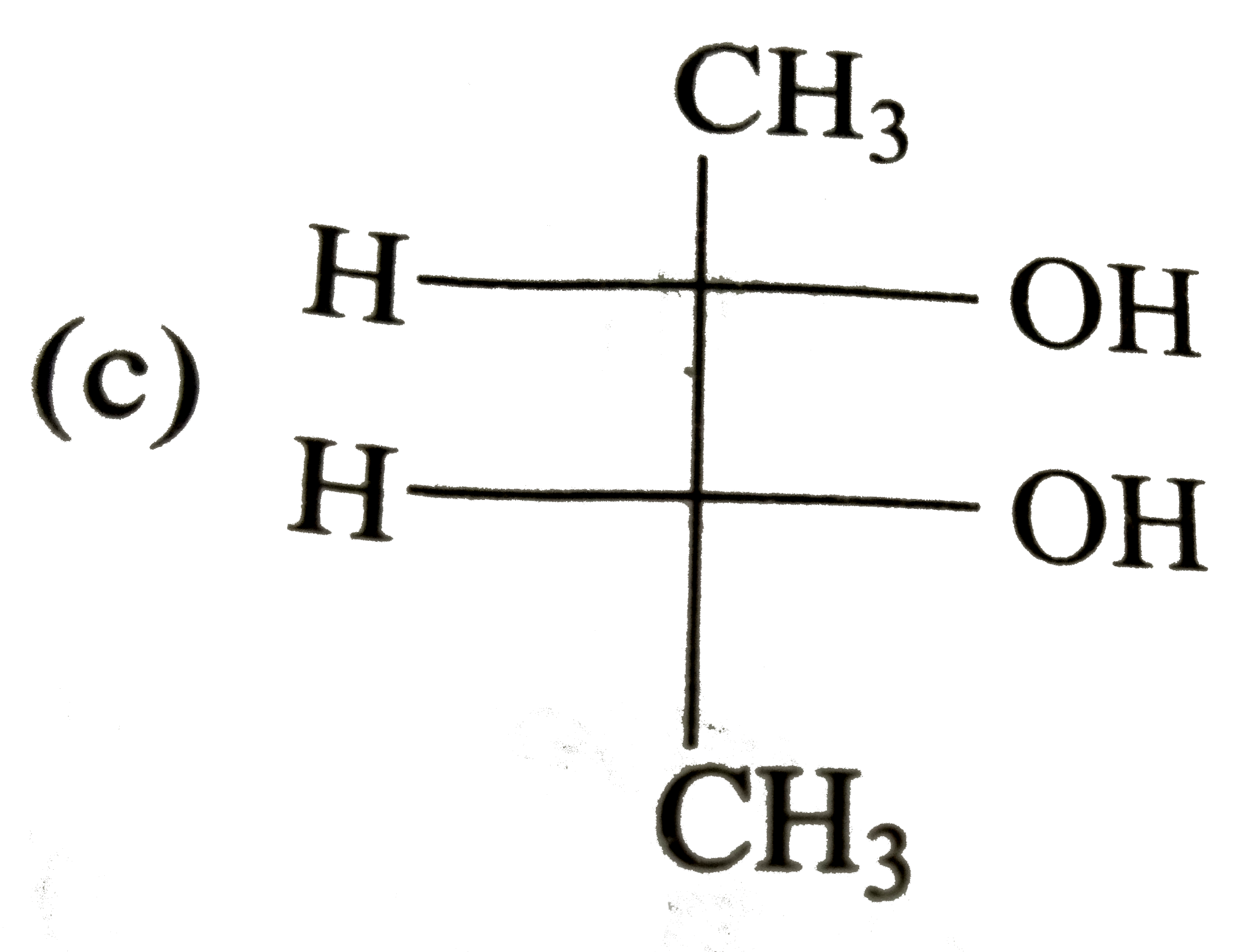
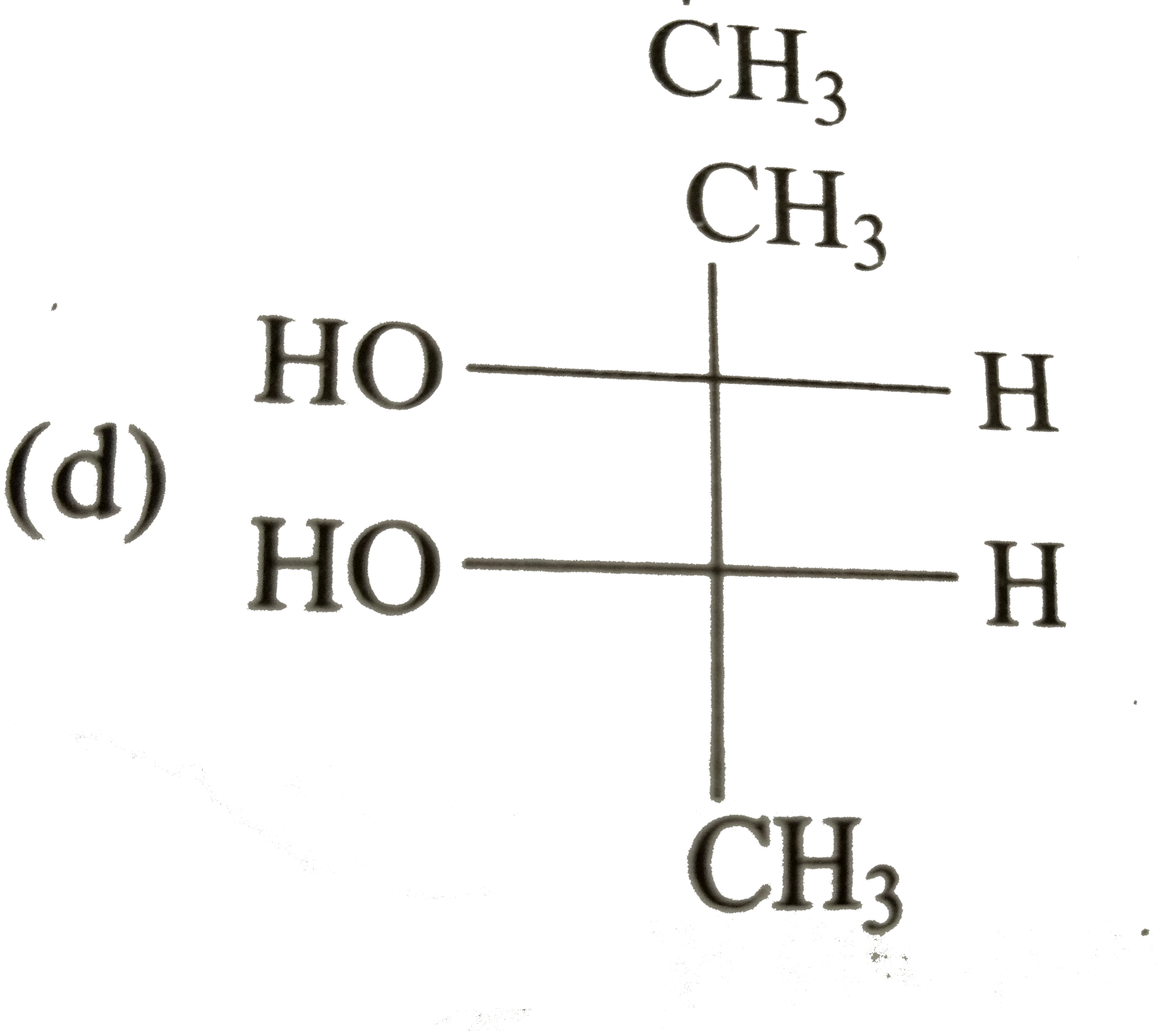
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ISOMERISM
HIMANSHU PANDEY|Exercise Level 3 (Q.26 To Q.50)|25 VideosISOMERISM
HIMANSHU PANDEY|Exercise Level 3 (Q.51 To Q.75)|25 VideosISOMERISM
HIMANSHU PANDEY|Exercise Level 2 (Q.51 To Q.55)|5 VideosHALIDES
HIMANSHU PANDEY|Exercise Subjective Type Problems|10 VideosNOMENCLATURE
HIMANSHU PANDEY|Exercise Section Iv (Q.26 To Q.26)|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
HIMANSHU PANDEY-ISOMERISM-Level 3 (Q.1 To Q.25)
- C(6)H(16) that can from cis trens isomerism and also chrial centre is
Text Solution
|
- Compound A below
Text Solution
|
- Following stereo-structure of trataric acid represents
Text Solution
|
- (2R,3r)-2,3 bantanediol is :
Text Solution
|
- Following eclipsed from propane is repeated after rotation of :
Text Solution
|
- What is iupac name of the following compound
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following will from geometrical isomers ?
Text Solution
|
- The number of enantiomers of the compound CH(3)-underset(Br)underset(|...
Text Solution
|
- The structure of (S) -2 -fluorobutane is best represented by :
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following compounds are meso forms ?
Text Solution
|
- The S-enantiomers of ibuprofen is reponsible for its pain-relieving pr...
Text Solution
|
- A naturally occurring substance has the constitution shown below. How ...
Text Solution
|
- Related the following compounds:
Text Solution
|
- Related the following compounds:
Text Solution
|
- Identify relation between these two compound
Text Solution
|
- Relate the following compounds
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following compounds is achrial
Text Solution
|
- The observed rotation of 2.0 gm of a compound iin 10 mL solution in a ...
Text Solution
|
- (+)-2 - Butanol has [theta](lambda)^(25)=+13.9^(@) A sample of 2- buta...
Text Solution
|
- In the structure the configuration at ahrial centres are :
Text Solution
|