Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MOTION-VECTOR & CALCULUS-EXERCISE -4 (LEVEL - II) PREVIOUS YEAR
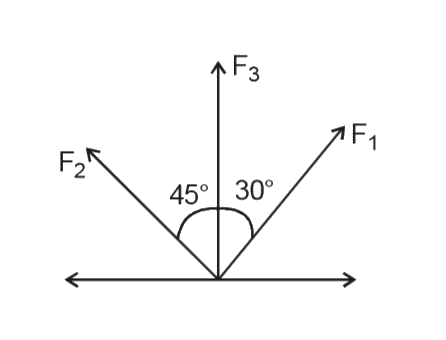
- Find the magnitude of F1 and F2. If F1, F2 make angle 30^@ and 45^@ wi...
Text Solution
|
- Three forces P,Q and R are acting at a point in the plane. The angle b...
Text Solution
|
- A man rows a boat with a speed of 18 km/hr in northwest direction. The...
Text Solution
|
- A bird moves from point (1, -2, 3) to (4, 2, 3). If the speed of the b...
Text Solution
|
- The resultant of two forces , one double the other in magnitude is pe...
Text Solution
|
- If the angle between the unit vectors hata " and " hatb is 60^(@), the...
Text Solution
|
- For a particle moving in a straight line, the displacement of the part...
Text Solution
|
- Two forces each numerically equal to 10 dynes are acting as shown in t...
Text Solution
|
- Two vectors vecA and vecB are such that vecA+vecB=vecA-vecB. Then
Text Solution
|
- A particle moves throught angular displacement theta on a circlur...
Text Solution
|
- The vector vecP makes 120^@ with the x-axis and vector Q makes 30° ...
Text Solution
|
- A man travels 1 mile due east. Then 5 miles due south, then 2 miles du...
Text Solution
|
- If 3hati+2hatj+8hatk and 2hati+xhatj+hatk are at right angles then x =
Text Solution
|
- a(1) hati+a(2)hatj is a unit vector perpendicular to 4hati - 3 hatj if...
Text Solution
|
- If vec(a) is a vector and x is a non-zero scalar, then
Text Solution
|
- Two vectors vecA and vecB are defined as vecA=ahati and vecB=a( cos om...
Text Solution
|