Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
KINEMATICS
MOTION|Exercise EXERCISE 1 OBJECTIVE PROBLEMS|103 VideosKINEMATICS
MOTION|Exercise EXERCISE 2 OBJECTIVE PROBLEMS|75 VideosHYDROSTATIC, FLUID MECHANICS & VISCOSITY
MOTION|Exercise EXERCISE -3 (SECTION-B) PREVIOUS YEAR PROBLEM|7 VideosKINETIC THEORY OF GASES
MOTION|Exercise EXERCISE-3 SECTION-B|16 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MOTION-KINEMATICS-EXERCISE 4 PREVIOUS YEAR (LEVEL 2)
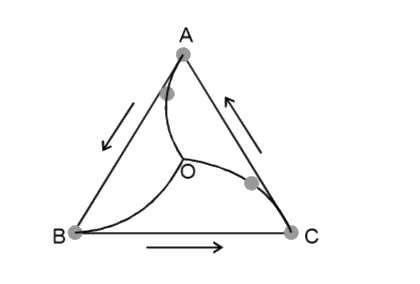
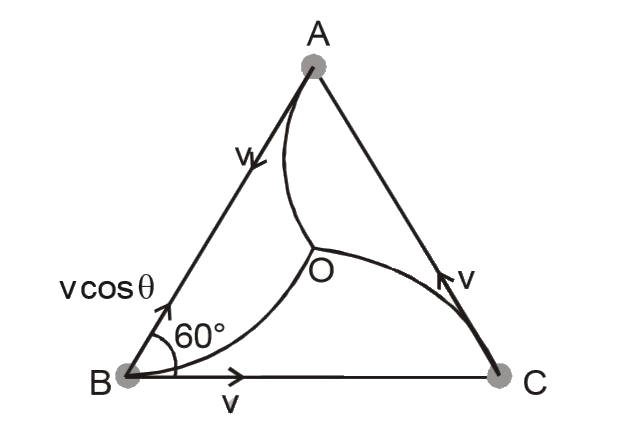
- Three particle A, B and C situated at the vertices of an equilateral t...
Text Solution
|
- The velocity - displacement graph of a particle moving along a straigh...
Text Solution
|
- STATEMENT -1 : For an observer looking out through the window of a fa...
Text Solution
|
- A train is moving along a straight line with a constant acceleration '...
Text Solution
|
- Airplanes A and B are flying with constant velocity in the same vertic...
Text Solution
|
- A rocket is moving in a gravity free space with a constnat acceleratio...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is thrown from ground at an angle theta with horizontal and wit...
Text Solution
|