Halogenation is a substitution reaction, where halogen replaces one or more hydrogens of hydrocarbon
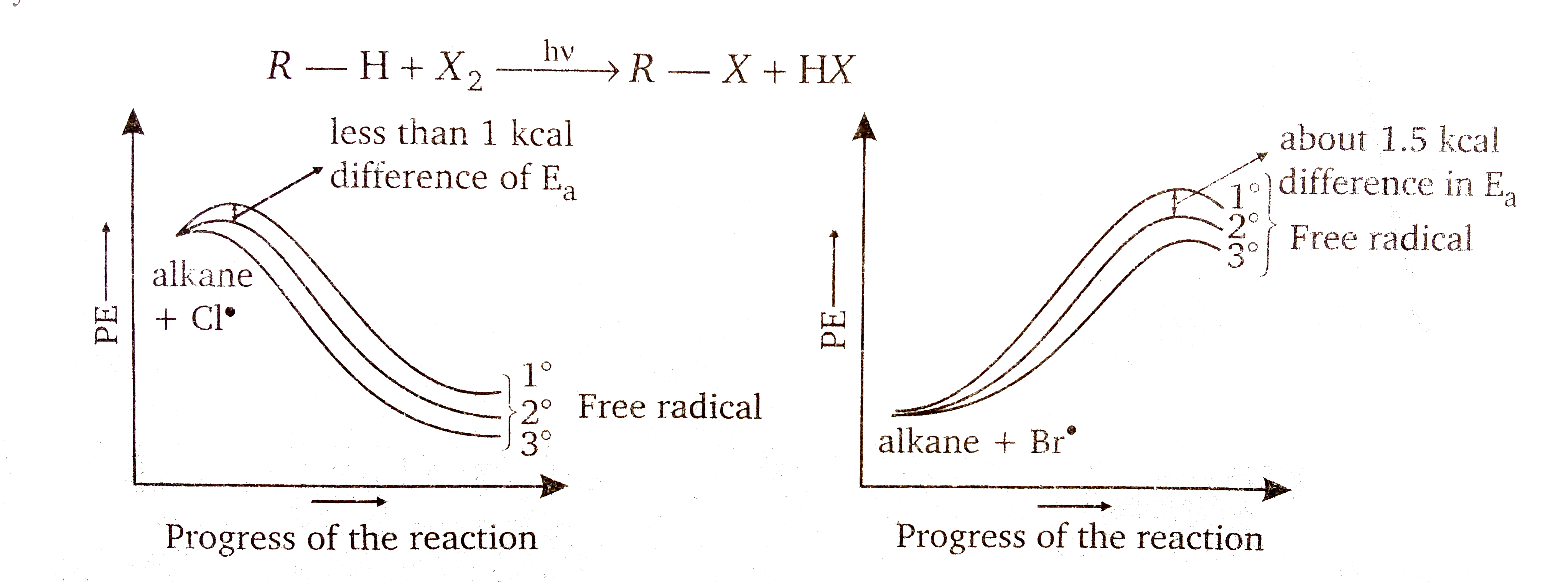
Chlorine free radical make `1^(@), 2^(@), 3^(@)` radicals with almost equal ease, whereas bromine free radicals have a clear preference for the formation of tertiary free radicals. So, bromine is less reactive, and more selectrive whereas chlorine is less selective and more reactive.
The relative rate of abstraction of hydrogen by `Br^(**)` is
`underset(1600)(3^(@)) gt underset(82)(2^(@)) gt underset(1)(1^(@))`
`underset(5)(3^(@)) gt underset(3.8)(2^(@)) gt underset(1)(1^(@))`
`CH_(3)-overset(CH_(3))overset(|)(CH)-CH_(3)overset(Cl_(2)//hv)(to)` product
Major product in the above reactio is:
Halogenation is a substitution reaction, where halogen replaces one or more hydrogens of hydrocarbon
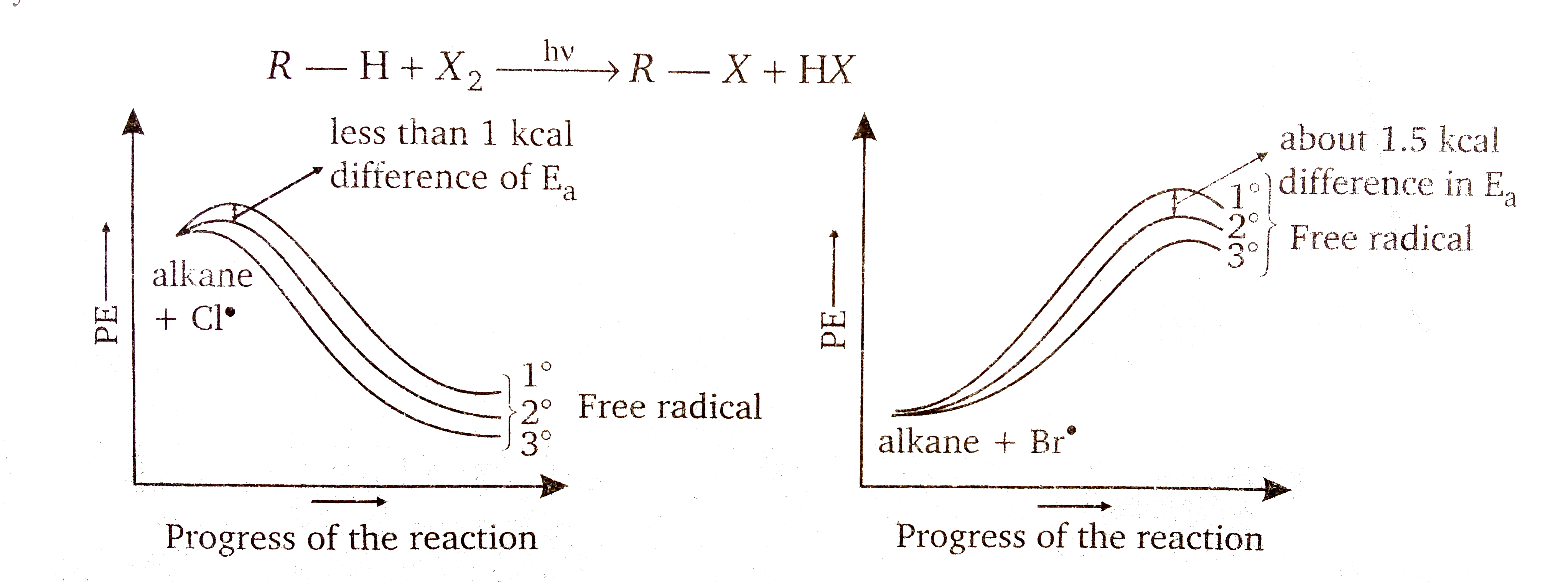
Chlorine free radical make `1^(@), 2^(@), 3^(@)` radicals with almost equal ease, whereas bromine free radicals have a clear preference for the formation of tertiary free radicals. So, bromine is less reactive, and more selectrive whereas chlorine is less selective and more reactive.
The relative rate of abstraction of hydrogen by `Br^(**)` is
`underset(1600)(3^(@)) gt underset(82)(2^(@)) gt underset(1)(1^(@))`
`underset(5)(3^(@)) gt underset(3.8)(2^(@)) gt underset(1)(1^(@))`
`CH_(3)-overset(CH_(3))overset(|)(CH)-CH_(3)overset(Cl_(2)//hv)(to)` product
Major product in the above reactio is:
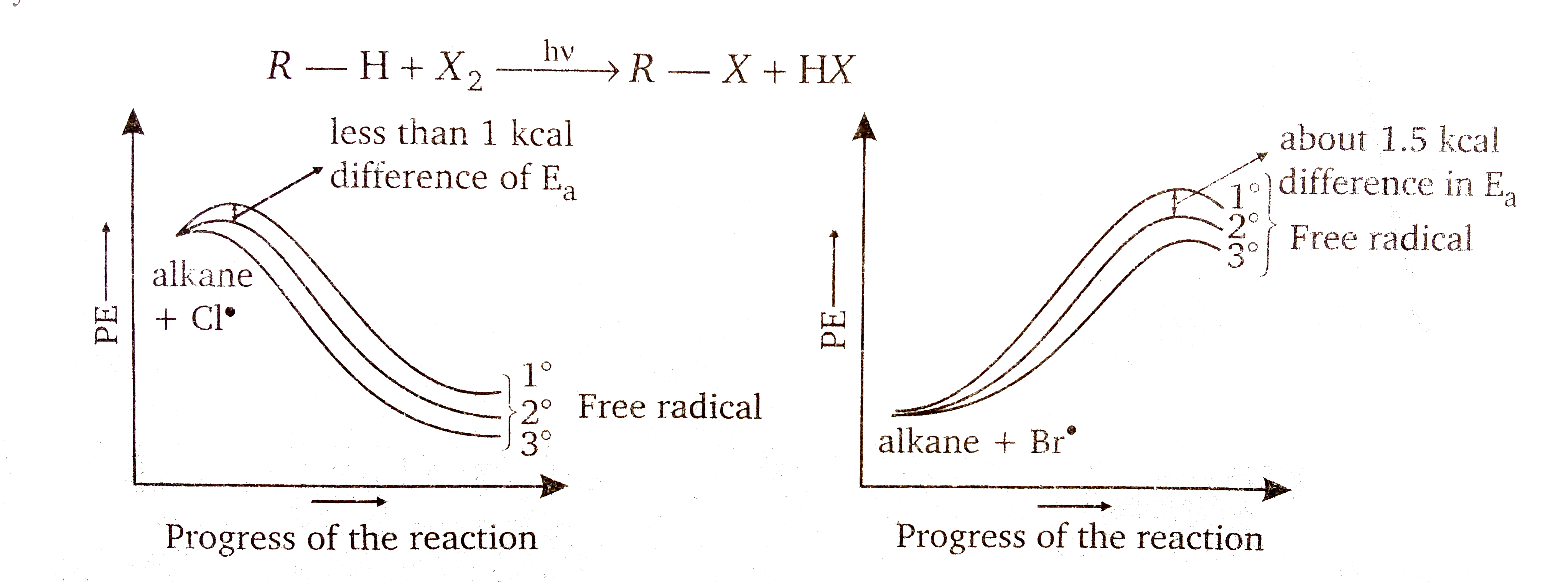
Chlorine free radical make `1^(@), 2^(@), 3^(@)` radicals with almost equal ease, whereas bromine free radicals have a clear preference for the formation of tertiary free radicals. So, bromine is less reactive, and more selectrive whereas chlorine is less selective and more reactive.
The relative rate of abstraction of hydrogen by `Br^(**)` is
`underset(1600)(3^(@)) gt underset(82)(2^(@)) gt underset(1)(1^(@))`
`underset(5)(3^(@)) gt underset(3.8)(2^(@)) gt underset(1)(1^(@))`
`CH_(3)-overset(CH_(3))overset(|)(CH)-CH_(3)overset(Cl_(2)//hv)(to)` product
Major product in the above reactio is:
A
`CH_(3)-overset(CH_(3))overset(|)(CH)-CH_(2)-Cl`
B
`CH_(3)-overset(CH_(3))overset(|)underset(Cl)underset(|)(CH)-CH_(3)`
C
`CH_(3)-CH_(2)-CH_(2)-Cl`
D
`CH_(3)-underset(Cl)underset(|)(CH)-CH_(2)-CH_(3)`
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
a
`o x-C-overset(C)overset(|)(C)-overset(C)overset(|)(C)-C`
`CH_(3)-overset(CH_(3))overset(|)(CH)-CH_(2)-Cl underset(1^(@))("Relative formation is") = 9xx1`, relative formation of `3^(@) = 5xx1`
`:.` %yield `= 9//14xx100`
`CH_(3)-overset(CH_(3))overset(|)(CH)-CH_(2)-Cl underset(1^(@))("Relative formation is") = 9xx1`, relative formation of `3^(@) = 5xx1`
`:.` %yield `= 9//14xx100`
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Halogenation is a substitution reaction, where halogen replaces one or more hydrogens of hydrocarbon Chlorine free radical make 1^(@), 2^(@), 3^(@) radicals with almost equal ease, whereas bromine free radicals have a clear preference for the formation of tertiary free radicals. So, bromine is less reactive, and more selectrive whereas chlorine is less selective and more reactive. The relative rate of abstraction of hydrogen by Br^(**) is underset(1600)(3^(@)) gt underset(82)(2^(@)) gt underset(1)(1^(@)) underset(5)(3^(@)) gt underset(3.8)(2^(@)) gt underset(1)(1^(@)) What is the value of x (% yield of product)?
Halogenation is a substitution reaction, where halogen replaces one or more hydrogens of hydrocarbon Chlorine free radical make 1^(@), 2^(@), 3^(@) radicals with almost equal ease, whereas bromine free radicals have a clear preference for the formation of tertiary free radicals. So, bromine is less reactive, and more selectrive whereas chlorine is less selective and more reactive. The relative rate of abstraction of hydrogen by Br^(**) is underset(1600)(3^(@)) gt underset(82)(2^(@)) gt underset(1)(1^(@)) underset(5)(3^(@)) gt underset(3.8)(2^(@)) gt underset(1)(1^(@)) Above product will obtained in better yield if X is
Halogenation is a substitution reaction, where halogen replaces one or more hydrogens of hydrocarbon Chlorine free radical make 1^(@), 2^(@), 3^(@) radicals with almost equal ease, whereas bromine free radicals have a clear preference for the formation of tertiary free radicals. So, bromine is less reactive, and more selectrive whereas chlorine is less selective and more reactive. The relative rate of abstraction of hydrogen by Br^(**) is underset(1600)(3^(@)) gt underset(82)(2^(@)) gt underset(1)(1^(@)) underset(5)(3^(@)) gt underset(3.8)(2^(@)) gt underset(1)(1^(@)) 1-halo-2,3-dimethyl butane will be obtained in better yields, if halogen is:
Halogenation is a substitution reaction, where halogen replaces one or more hydrogens of hydrocarbon Chlorine free radical make 1^(@), 2^(@), 3^(@) radicals with almost equal ease, whereas bromine free radicals have a clear preference for the formation of tertiary free radicals. So, bromine is less reactive, and more selectrive whereas chlorine is less selective and more reactive. The relative rate of abstraction of hydrogen by Br^(**) is underset(1600)(3^(@)) gt underset(82)(2^(@)) gt underset(1)(1^(@)) underset(5)(3^(@)) gt underset(3.8)(2^(@)) gt underset(1)(1^(@)) How many dichloro products (including stereoisomers) will be formed when R-2-chloropentane reacts with Cl_(2) in presence of UV radiation?
Halogenation is a substitution reaction, where halogen replaces one or more hydrogens of hydrocarbon Chlorine free radical make 1^(@), 2^(@), 3^(@) radicals with almost equal ease, whereas bromine free radicals have a clear preference for the formation of tertiary free radicals. So, bromine is less reactive, and more selectrive whereas chlorine is less selective and more reactive. The relative rate of abstraction of hydrogen by Br^(**) is underset(1600)(3^(@)) gt underset(82)(2^(@)) gt underset(1)(1^(@)) underset(5)(3^(@)) gt underset(3.8)(2^(@)) gt underset(1)(1^(@)) Which of the following will give five monochloro products, when allowed to react with Cl_(2) in presence of sun light (excluding stereoisomers)?
Halogenation is a substitution reaction, where halogen replaces one or more hydrogens of hydrocarbon Chlorine free radical make 1^(@), 2^(@), 3^(@) radicals with almost equal ease, whereas bromine free radicals have a clear preference for the formation of tertiary free radicals. So, bromine is less reactive, and more selectrive whereas chlorine is less selective and more reactive. The relative rate of abstraction of hydrogen by Br^(**) is underset(1600)(3^(@)) gt underset(82)(2^(@)) gt underset(1)(1^(@)) underset(5)(3^(@)) gt underset(3.8)(2^(@)) gt underset(1)(1^(@)) What would be the product ratio x/y in the chlorination of propane if all the hydrogen were abstracted at equal rate? CH_(3)-CH_(2)-CH_(3)overset(Cl_(2))underset(hv)(to)CH_(3)-CH_(2)-underset((x))underset()underset()(CH_(2))-Cl+CH_(3)-underset((y))underset(Cl)underset(|)CH-CH_(3)
Free Radical
Free radicals have ___.
Formation of free radical is eaisest in: