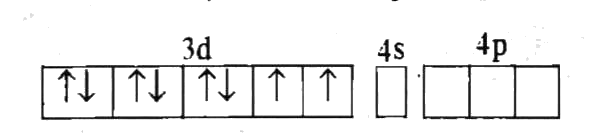
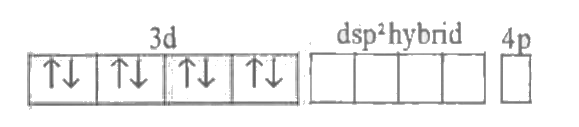
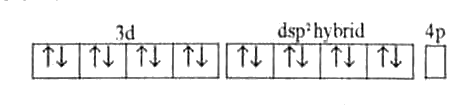Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
SUBHASH PUBLICATION-CO-ORDINATION COMPOUNDS-Questions
- Draw cis nd trans isomers of [Co(NH(3))(4)Cl(2)]^(+) ion.
Text Solution
|
- Draw the structures of geometrical isomers of [Fe(NH(3))(2)(CN)(4)]^-.
Text Solution
|
- Draw the structures of geometrical isomers of [CoCl(2)(en)(2)]^(+).
Text Solution
|
- Give the facial (fac) and meridional (mer) isomeric structures of [Co(...
Text Solution
|
- Draw the optical isomers of [CO(en)(3)]^(2+).
Text Solution
|
- Draw the optical isomers of [Pt(Cl)(2)(en)(2)]^(2+).
Text Solution
|
- Draw the optical isomers of [CrCl(2)("ox")(2)]^(2-).
Text Solution
|
- Explain ionisation isomerisation with an example.
Text Solution
|
- What is likage isomerism ? Explain with an example.
Text Solution
|
- What is an ambidentate ligand ? Name the type of structural isomerism ...
Text Solution
|
- Describe the structure and magnetic behaviour of [Ni(CN)4]^(2-) ion on...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the hybridisation, geometry and magnetic property of [Ni(Cl)(4...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the hybridisation, geometry and magnetic prpoperty of [Co(NH(3...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the hybridisation, geometry and magnetic property of [CoF(6)]^...
Text Solution
|
- [NiCl(4)]^(-2) and [Ni(CN)(4)]^(-2) resemble in
Text Solution
|
- [Co(NH(3))(6)]^(3+) & [CoF(6)]^(3-) both are complexes of Co(III), but...
Text Solution
|
- Which set of d-orbitals of metals ion or atom experience more repulsio...
Text Solution
|
- When a linkage isomerism is possible for co-ordination compounds ?
Text Solution
|
- Indicate the types of isomerism exhibited by the follow complexes and ...
Text Solution
|
- According to crystal filed theory , five d-orbitals of an octahedral c...
Text Solution
|