Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
SUBHASH PUBLICATION-HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES-Questions
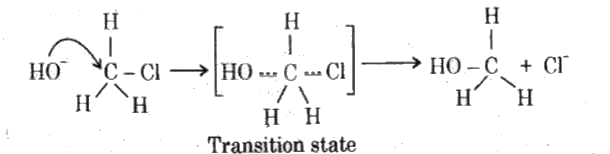
- Give examples to show that alkyl halides undergoes nucleophilic substi...
Text Solution
|
- Explain S(N) - 1 reaction mechanism.
Text Solution
|
- Explain S(N) - 2 reaction mechanism ?
Text Solution
|
- Give two differences between S(N) - 1 and S(N) - 2 mechainsm.
Text Solution
|
- What is optical activity ? Explain.
Text Solution
|
- What is asymmetric carbon atom.
Text Solution
|
- What is chirality ?
Text Solution
|
- What are enantiomers? Give example.
Text Solution
|
- What are enantiomers ?
Text Solution
|
- What is racemic mixture ?
Text Solution
|
- Explain elimination reaction. Give example.
Text Solution
|
- Explain elimination reaction. Give example.
Text Solution
|
- State Saytzeff rule. Give example.
Text Solution
|
- Name the reagent used in the dehydrohalogenation of haloalkanes.
Text Solution
|
- Name the major product obtained when tertiary butyl bromide is heated ...
Text Solution
|
- Which gas is liberated when 2-Bromopropene is heated with alcoholic po...
Text Solution
|
- Write the IUPAC name of the major product obtained when 2-Bromopentane...
Text Solution
|
- What are Grignard reagents ? Give example.
Text Solution
|
- Aryl halides are less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution react...
Text Solution
|
- Give the conversion chlorobenzene to phenol.
Text Solution
|