A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
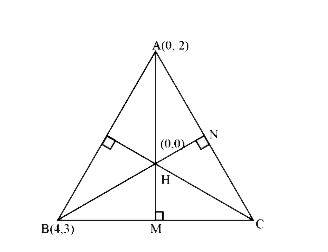
- If two vertices of a triangle are (0,2) and (4,3) and its orthocentre ...
Text Solution
|
- From the point (2, 2) tangent are drawn to the hyperbola (x^2)/(16)-(y...
Text Solution
|
- A point whose abscissa and ordinate are 2 and -5 respectively, lies ...
Text Solution
|
- The abscissa of a point is positive in the (a) First and Second qu...
Text Solution
|
- A point whose abscissa is -3\ and ordinate 2 lies in (a) First quad...
Text Solution
|
- If two vertices of a triangle are (0,2) and (4,3) and its orthocentre ...
Text Solution
|
- If a complex number lies in third quadrant ,then its conjugate lies in...
Text Solution
|
- The common region represented by xle4,x-yge0,3x+yge3 lies fully in a...
Text Solution
|
- The abscissa of a point is positive in the First and Second quad...
Text Solution
|