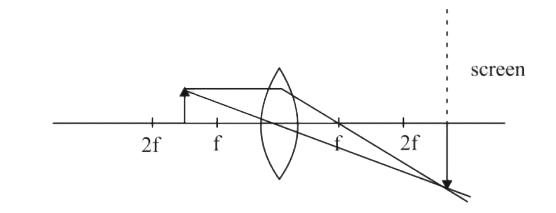
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Formation of real image using a biconvex lens is shown below : If...
Text Solution
|
- if you focus the image of a distant object, whose shape is given belo...
Text Solution
|
- A convex lens when placed in the first position forms a real image of ...
Text Solution
|
- A convex lens makes a real image 4 cm long on a screen. When the lens ...
Text Solution
|
- Formation of real image using a biconves lens is shown below: If...
Text Solution
|
- Formation of real image using a biconves lens is shown below: If the w...
Text Solution
|
- The image of an object formed by a lens on the screen is not in sharp ...
Text Solution
|
- Formation of real image using a biconvex lens is shown below : If the ...
Text Solution
|
- A convex lens forms a real image 16 mm long on a screen. If the lens i...
Text Solution
|