A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
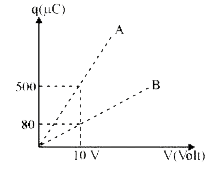
- Figure shows charge (q) versus voltage (V) graph for series and parall...
Text Solution
|
- Two capacitor each having capacitance Cand breakdown voltage Vare join...
Text Solution
|
- Three capacitors each of capacitance C and of breakdown voltage V are ...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical capacitors are connected in series with a source of cons...
Text Solution
|
- Two capacitors of capacitances C1" and "C2, are connected in parallel....
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows charge (q) versus voltage (V) graph for series and parall...
Text Solution
|
- The energy stored in a capacitor is given by (V = Voltage, C = Capacit...
Text Solution
|
- C1 धारिता के एक संधारित्र को V विभव से आवेशित किया जाता है तथा फिर C2 ...
Text Solution
|
- दो दिए गए संधारित्रों को श्रेणी तथा समान्तर क्रम में लगाने पर उनका आवे...
Text Solution
|