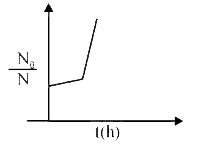
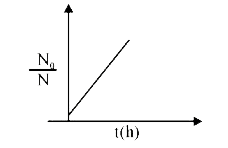
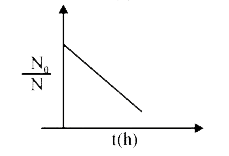
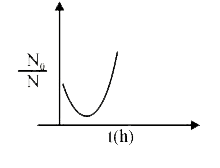
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A bacterial infection in an internal wound grows as N'(t) = N(0) exp (...
Text Solution
|
- Growth of a bacteria is represented as N(t)=N(0)e^(lamdat) After one h...
Text Solution
|
- If N = population density at time t, then population density at time t...
Text Solution
|
- The equations (dN)/(dt) = - lambda N and N = N(0)e^(- lambda t) descri...
Text Solution
|
- If N(0) and N are the number of radioactive particles at time t = 0 an...
Text Solution
|
- किसी क्षण t पर संख्या N (t ) की वृद्धि (dN(t) )/(dt)=alpha N(t) द्वार...
Text Solution
|
- If m, n in R, then the value of I(m,n)=int(0)^(1) t^(m)(1+t)^(n)dt is...
Text Solution
|
- Show that N=(N(0))/(2^(n)) where n = number of half lives n=t/T
Text Solution
|
- A bacterial infection in an internal wound grows as N'(t) = N(0) exp (...
Text Solution
|