Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- The total number of isomers for a square planer complex [M(F)(Cl)(SCN)...
Text Solution
|
- Total number of possible isomers of complex [Pd(NH(3))(2)(SCN)(2)]
Text Solution
|
- A square planer complex represented as :
Text Solution
|
- The total number of isomers of a square planer complex [M(F)(CI)(SCN)(...
Text Solution
|
- The total number of possible isomers of sqaure-planar [Pt(Cl)(NO(2))(N...
Text Solution
|
- The number of isomers possbile for square planar complex K(2)[PbClBr(2...
Text Solution
|
- The total number of isomers for a square planer complex [M(F)(Cl)(Br)(...
Text Solution
|
- The total number of isomers for a square planer complex [M(F)(Cl)(SCN)...
Text Solution
|
- The number of geometric isomers that can exist for square planner comp...
Text Solution
|
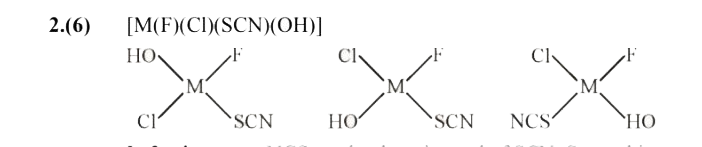 In 3 other cases NCS can be there instead of SCN. So total isomer = 6
In 3 other cases NCS can be there instead of SCN. So total isomer = 6