Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
GRB PUBLICATION-MOTION IN TWO AND THREE DIMENSIONS-All Questions
- Two towers AB and CD are situated a distance d apart as shown in Fig. ...
Text Solution
|
- An object of mass 5 kg is projecte with a velocity of 20ms^(-1) at an ...
Text Solution
|
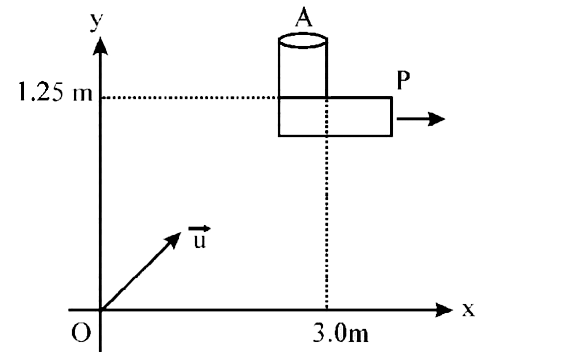
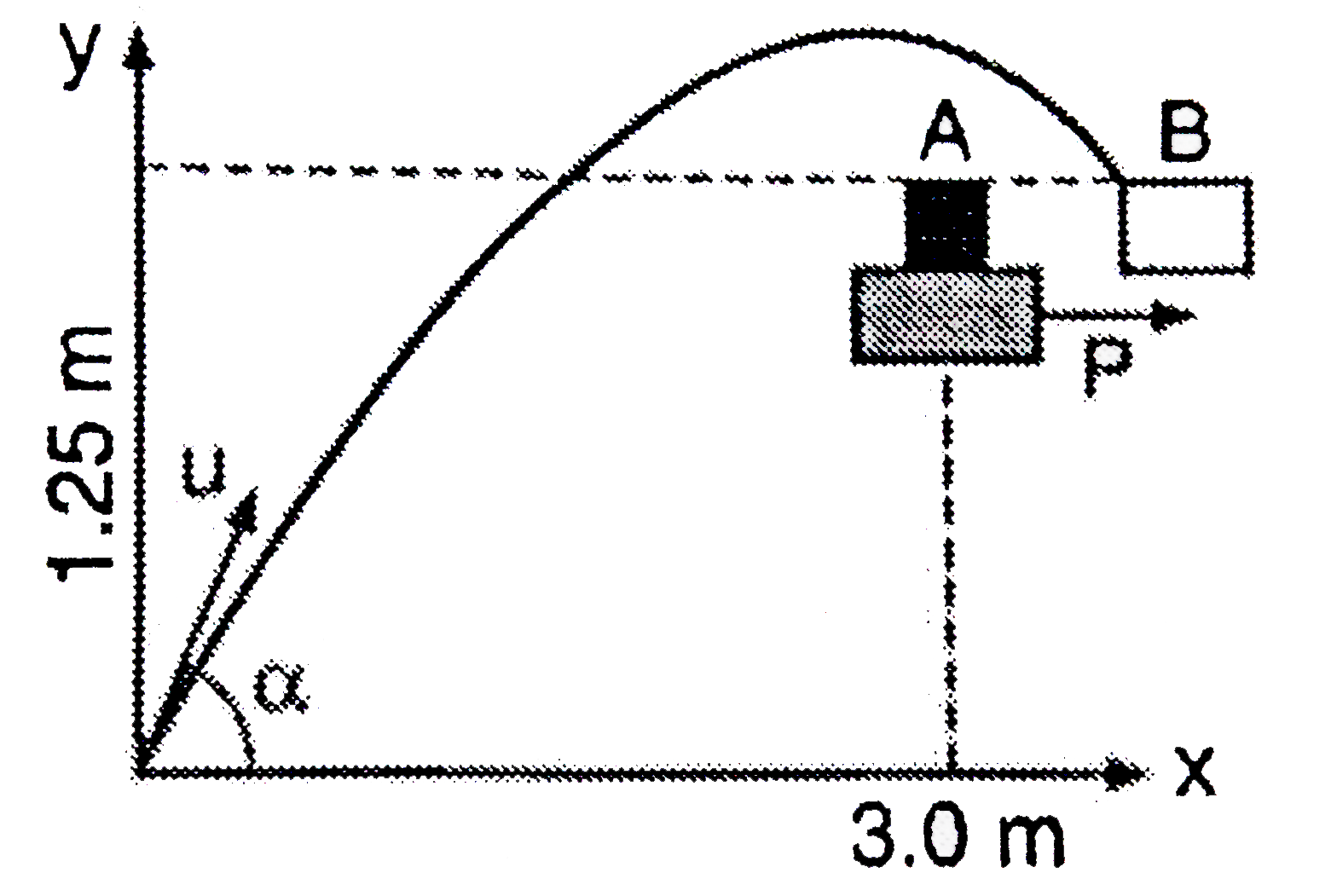
- An object A is kept fixed at the point x= 3 m and y = 1.25 m on a pl...
Text Solution
|
- A body falling freely from a given height H hits an inlclined plane in...
Text Solution
|
- A rocket moves horizontally with a constant velocity u at a height 1. ...
Text Solution
|
- A man swims with avelocity v(mw) in still water. When the water moves ...
Text Solution
|
- If the radius of earth is 6400km, calcu late (a) angu lar velocity (b)...
Text Solution
|
- An astronaout is rotating in a rotor of radius 4m. If he can withstand...
Text Solution
|
- Two satellites S(1) and S(2) revolve around a planet in coplanar circu...
Text Solution
|
- A threaded rod with 12 turns//cm and diameter 1.18 cm is mounted horiz...
Text Solution
|
- A wheel having radius 10cm is coupled by a belt to another wheel of ra...
Text Solution
|
- A spot light S rotates in a horizontal plane with a constant angular v...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is projected with a velocity vecv=ahati+bhatj. Find the rad...
Text Solution
|
- A balloon starts rising from the earth's surface. The ascension rate i...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles of masses m(1) and m(2) are initially at rest infinite d...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass 10^-2kg is moving along the positive x axis under t...
Text Solution
|
- A body projected vertically upwords from the top of a tower reaches th...
Text Solution
|
- (a) सिद्ध कीजिए कि किसी प्रक्षेप्य के x - अक्ष तथा उसके वेग के बिच ...
Text Solution
|
- What is the displacement of the point of a wheel initially in contact ...
Text Solution
|
- The horizontal and vertical distances covered by a projectile at tiem ...
Text Solution
|