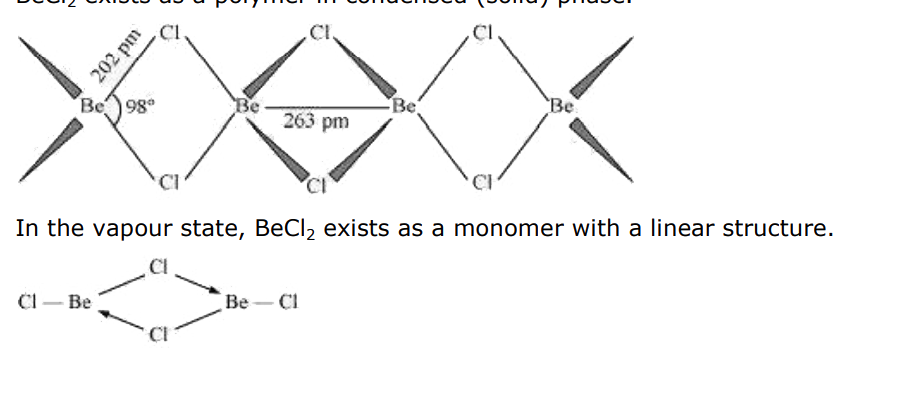Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT-THE S-BLOCK ELEMENTS-EXERCISE
- Why potassium carbonate (K(2)CO(3)) cannot be prepared by Solvay-ammon...
Text Solution
|
- Why is Li(2)CO(3) decomposed at a lower temperature whereas Na(2)CO(3)...
Text Solution
|
- Compare the solubility and thermal stability of the following compound...
Text Solution
|
- Starting with sodium chloride how would you proceed to prepare: (a) s...
Text Solution
|
- What happens when (a) magensium in burnt in air, (b) quicklime is heat...
Text Solution
|
- Describe two important uses of each of the following: (a) casutic so...
Text Solution
|
- Draw the structure of (a) BeCl(2)(vapour) and (b) BeCl(2) (solid).
Text Solution
|
- The hydroxides and carbonates of sodium and potassium are easily solub...
Text Solution
|
- Describe the importance of the following: (a) limestone, (b) cement an...
Text Solution
|
- Why are lithium salts commonly hydrated and those of the other alkali ...
Text Solution
|
- Why is LiF almost insoluble in water whereas LiCl soluble not only in ...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the significance of sodium, potassium, magnesium and calcium o...
Text Solution
|
- What happens when a. Sodium metal is dropped in water? b. Sodium m...
Text Solution
|
- Comment on each of the following observation: a. The mobilities of t...
Text Solution
|
- State as to why (a) a solution of Na(2)CO(3) is alkaline ? (b) alk...
Text Solution
|
- Write balanced equations for reactions between a. Na(2)O(2) and wate...
Text Solution
|
- How would you explain the following observations ? (i) BeO is almost...
Text Solution
|
- .Which of the alkali metal is having least melting point?
Text Solution
|
- Which one of the following alkali metals gives hydrated salts?
Text Solution
|
- Which one of the alkaline earth metal carbonates is thermally the most...
Text Solution
|