Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT-SURFACE CHEMISTRY-Exercise
- Give reason why a finely divided substance is more effective as an ads...
Text Solution
|
- What are the factors which influence the adsorption of a gas on a soli...
Text Solution
|
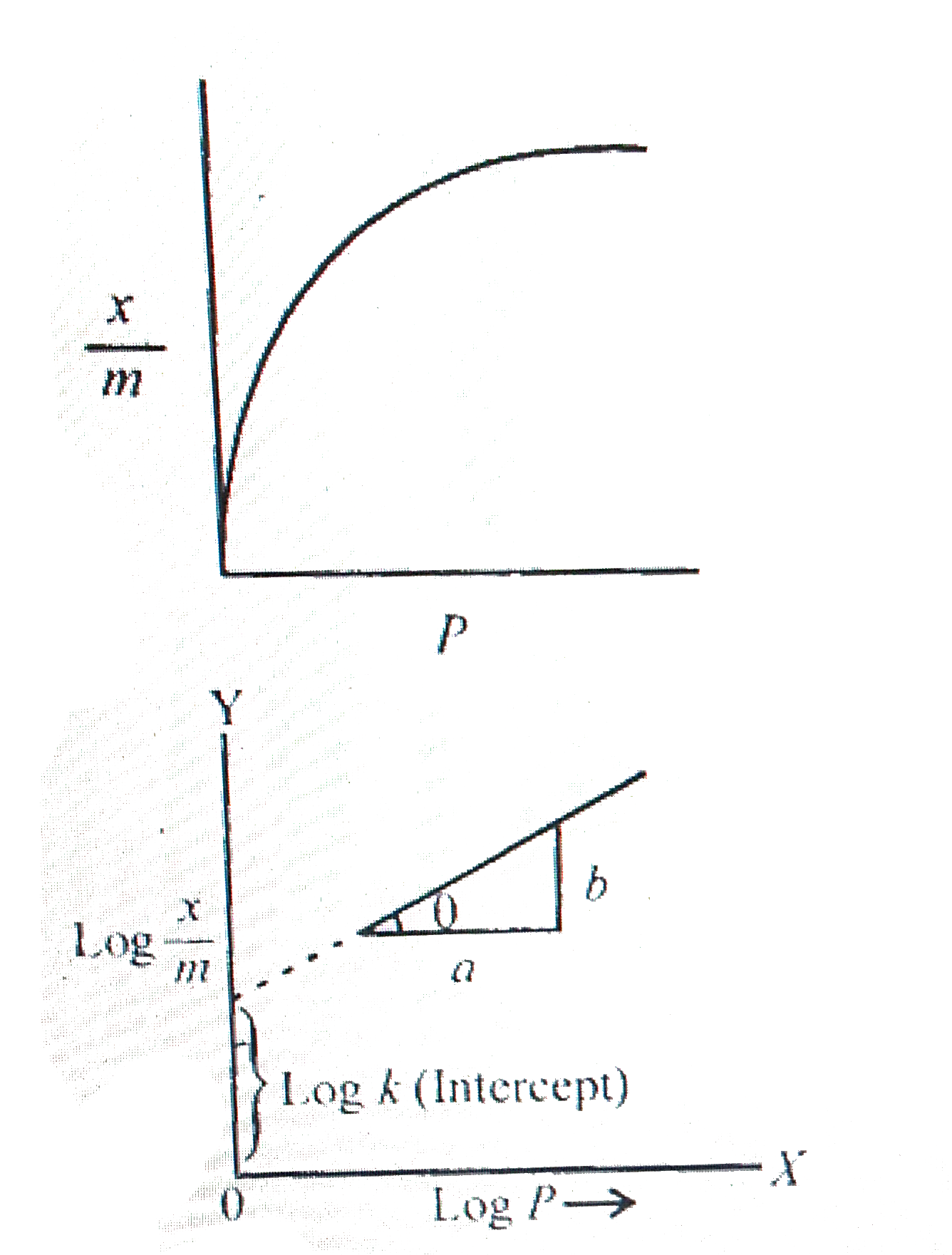
- What is an adsorption isotherm? Describe Freundlich adsorption isother...
Text Solution
|
- What do you understand by activation of adsorption ? How is it achieve...
Text Solution
|
- What role does adsorption play in heterogeneous catalysis ?
Text Solution
|
- Why is adsorption always exothermic ?
Text Solution
|
- How are the colloidal solutions classified on the the basis of physica...
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the effect of pressure and temperature on the adsorption of ga...
Text Solution
|
- What are lyophilic and lyophobic sols?Give one example of each type ? ...
Text Solution
|
- What is the difference between multimolecular and macromolecular colli...
Text Solution
|
- What are enzymes ? Write in brief the mechanism of enzyme catalysis ?
Text Solution
|
- How are colloids classified on the basis of (i) physical states of c...
Text Solution
|
- Explain what is observed (i) when a beam of light is passed through ...
Text Solution
|
- What are emulsions ? What are their different types ? Give an example ...
Text Solution
|
- How do emulsifiers stabilise emulsion ? Name two emulsifiers.
Text Solution
|
- Action of soap is due to emulsification and micelle formation. Comment...
Text Solution
|
- Give four examples of heterogeneous catalytic reactions.
Text Solution
|
- What do you mean by activity and selectivity of catalysts ?
Text Solution
|
- Descirbe some features of catalysis by zeolites.
Text Solution
|
- What is shape selective catalysis ?
Text Solution
|