Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT-ELECTROSTATIC POTENTIAL AND CAPACITANCE-Exercise
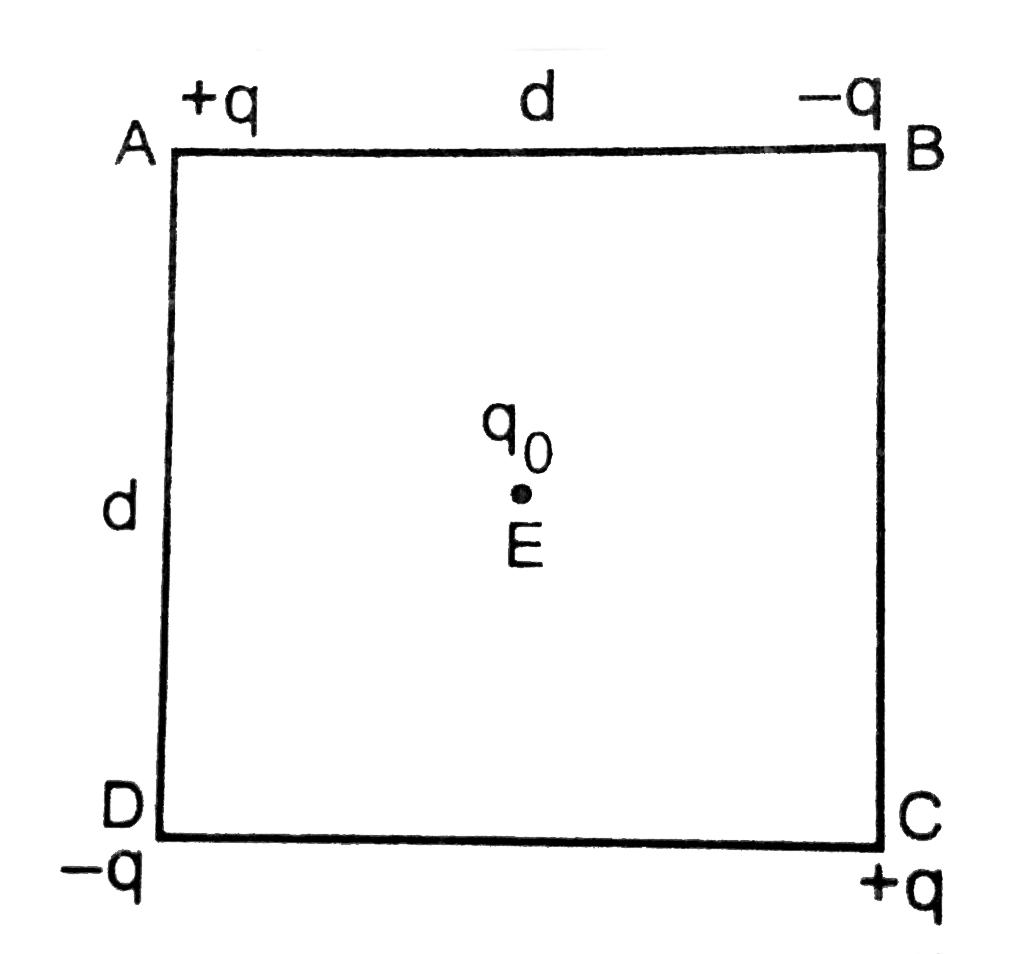
- Four charges are arranged at the corners of a square ABCD of side d,...
Text Solution
|
- Two charges 5xx10^(-8)C and -3xx10^(-8)C are located 16 cm apart. At ...
Text Solution
|
- A regular hexagon of side 10 cm has a charge 5 muC at each of its ver...
Text Solution
|
- Two charges + 2 muC and -2 muC are placed at points A and B, 6 cm apa...
Text Solution
|
- A spherical conductor of radius 12 cm has a charge of 1.6xx10^(-7)C ...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel plate capacitor with air between the plates has a capacit...
Text Solution
|
- Three capacitors each of capacitance 9 pF are connected in series. (...
Text Solution
|
- Three capacitors of capacitance 2 pF, 3 pF and 4 pF are connected in...
Text Solution
|
- In a parallel plate capacitor with air between the plates, each plate...
Text Solution
|
- Explain what would happen if a 3 mm thick mica sheet of (dielectric ...
Text Solution
|
- A 12 pF capacitor is connected to a 50 V battery. How much electrost...
Text Solution
|
- A 600 pF capacitor is charged by a 200 V supply. It is then disconnect...
Text Solution
|
- A charge of 8 mC is located at the origin. Calculate the work done in ...
Text Solution
|
- A cube of side b has a charge q at each of its vertices. Determine the...
Text Solution
|
- Two tiny spheres carrying charges 1.5 muC and 2.5 muC are located 30 c...
Text Solution
|
- A spherical conducting shell of inner radius r(1) and outer radius r(2...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Show that the normal component of electrostatic field has a discon...
Text Solution
|
- A long charged cylinder of linear charge density lambda is surrounde...
Text Solution
|
- In a hydrogen atom, the electron and proton are bound at a distance of...
Text Solution
|
- If one of the two electrons of a hydrogen molecule is removed, we get ...
Text Solution
|
- Two charged conducting spheres of radii a and b are connected to eac...
Text Solution
|