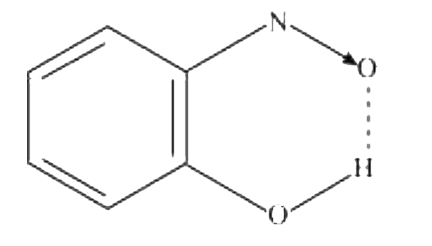
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT-CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE-EXERCISE
- Apart from tetrahedral geometry, another possible geometry for CH(4) i...
Text Solution
|
- Explain why BeH(2) molecule has a zero dipole moment although the Be-H...
Text Solution
|
- Out of NH(3) and NF(3) which has a higher Dipole moment?
Text Solution
|
- What is meant by hybridisation of atomic orbitals? Describe the shape ...
Text Solution
|
- Describe the change in hybridization (if any) of the Al atom in the fo...
Text Solution
|
- Is there any change in hybridisation of the B and N atom as a result o...
Text Solution
|
- Draw diagrams showing the formation of a double bond and a triple bond...
Text Solution
|
- What is the total number of sigma and pi bonds in the following molecu...
Text Solution
|
- Considering X axis as the inter nuclear axis, which out of the followi...
Text Solution
|
- Which hybrid orbitals are used by carbon atoms in the following molecu...
Text Solution
|
- What do you understand by bond pairs and lone pairs of electrons? Illu...
Text Solution
|
- Distinguish between a sigma and a pi bond.
Text Solution
|
- Explain the formation of H(2) molecule on the basis of valence bond th...
Text Solution
|
- Write the important conditions required for the linear combination of ...
Text Solution
|
- Use molecular orbital theory to explain why the Be(2) molecules do not...
Text Solution
|
- Compare the relative stability of the following species and indicate t...
Text Solution
|
- Write the significance of a plus and a minus sign shown in representin...
Text Solution
|
- Describe the hydribisation in case of PCl(5). Why are the axial bonds ...
Text Solution
|
- Define hydrogen bond. Is it weaker or stronger than the van der Waals ...
Text Solution
|
- What is meant by the term bond order? Calculate the bond order of N(2)...
Text Solution
|