Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT-THE P-BLOCK ELEMENTS -EXERCISE
- Rationalise the given statements and give chemical reactions. a. Lea...
Text Solution
|
- Suggest reasons why the B–F bond lengths in BF(3) (130 pm) and BF(4 )^...
Text Solution
|
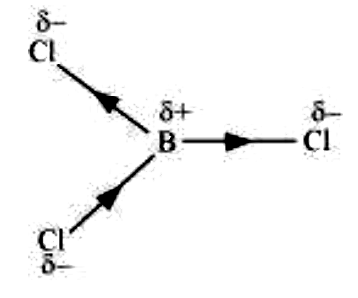
- If B-Cl bond has a dipole moment, explain why BCl(3) molecule has zero...
Text Solution
|
- AlF(3) is insoluble in anhydrous HF but dissolves on addition of NaF. ...
Text Solution
|
- Suggest a reason as to why CO is poisonous.
Text Solution
|
- How is excessive content of CO(2) responsible for global warming?
Text Solution
|
- Explain structures of diborane and boric acid.
Text Solution
|
- What happens when (a) Borax is heated strongly, (b) Boric acid is ...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the following reactions (a) Silicon is heated with methyl ch...
Text Solution
|
- Give reasons : (i) Conc. HNO(3) can be transported in aluminium con...
Text Solution
|
- Explain why is there a phenomenal decrease in ionisation enthalpy from...
Text Solution
|
- How would you explain the lower atomic radii of Ga as compared to Al?
Text Solution
|
- What are allotropes? Sketch the structure of two allotropes of carbon ...
Text Solution
|
- a. Classify following oxides as neutral, acidic, basic or amphoteric: ...
Text Solution
|
- In some of the reactions, thallium resembles aluminium whereas in othe...
Text Solution
|
- When metal X is treated with sodium hydroxide, a white precipitate (A)...
Text Solution
|
- What do you understand by (a) inert pair effect (b) allotropy and (c...
Text Solution
|
- A certain salt (X) gives the following tests : (a) Its aqueous solut...
Text Solution
|
- Write balanced equations for: a.BF(3)+LiHto b.B(2)H(6)+H(2)Oto c...
Text Solution
|
- Give one method for industrial preparation and one for laboratory prep...
Text Solution
|