As shown in fig. In the relation of dipole moment to configuraion is quite direct. If in a 1,2 -disubstitued alkene (XY=CYZ) X and Y are both electron donating or both electrons withdrawing , the dipole moment of the cis isomer will generally be sizeble whereas that of the trans isomer will be small or zero `(i.e.,mu_("cis")gtmu_("trans"))`. If on the other hand, X is electron donating and Y is electron withdrawing of vice versa, `mu_("trans")gtmu_("cis")`. In tribustituted alkenes XCH=CYZ the situation is less clear cut, though if Z is alkyl and X and Y are hologen or other strongly electron withdrawing groups, the disposition (cis or trans)
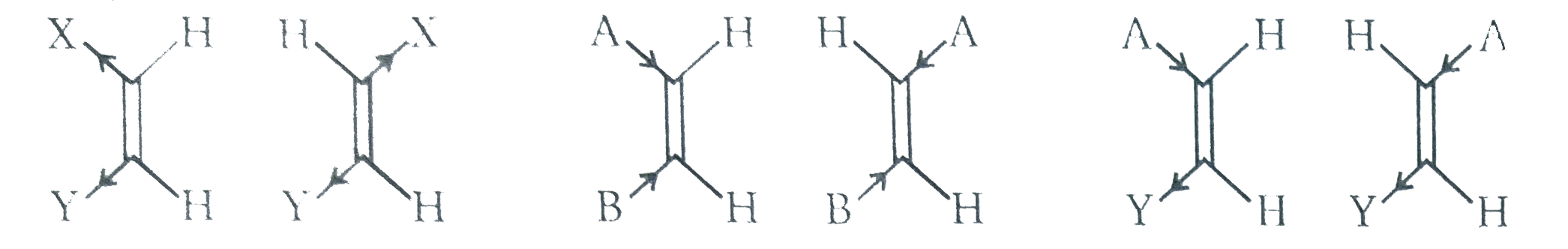
of X and Y will be decisive, Except for the case of cyclooctene, configuration can be inferred form dipole moment where known the differences are perhaps uncomfortably small. In the case of 1-chloro-2-iodoethylene the original,seemingly unresonable order of dipole moments was later reversed . In trans-cyclooctene, the normal `C_(2h)` symmetry of trans-XCH=CHY is reduced to at most `C_(2)`, threrefore the compound can have a dipole moment, whereas compound of `C_(2h)` symmetry cannot. That the moment is so large may be releated to the highly twisted nature of the dipole bond (torsion angle between `136^(@) and 157^(@))`
Dipole Moments and the Dopole `"Rule"^(a)`:
As for as the question is concerned, melting point of (trans `gt` cis) because trans from is more symmetrical than cis from .