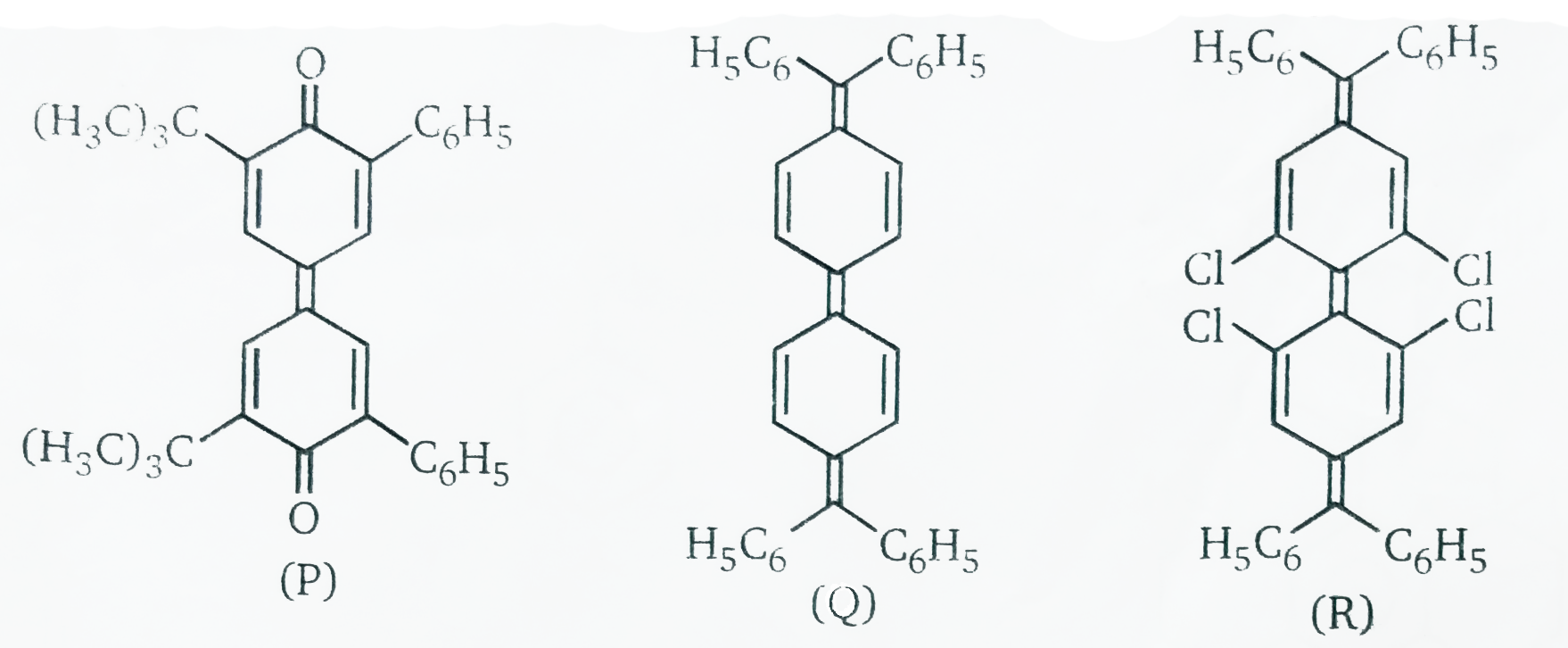
In some alkenes, steric crowding in the planar state may be so severe that the latter is no longer an energy minimum but becoms an energy barrier with the ground state becoming twisted. In this contex the compounds in figure are of interest. The drop in becoming twisted. In this contex the compounds in fiugure are of intrest. The drop in rotational barrier from stilbene `(42.8 "kcal//mol"^(-1), 179 kJ "mol"^(-1))` to compound p `(21.1 "lcal //mol"^(-1),88.3 kJ "mol"^(-1))` to compound Q ("small barrier" , ct) may be explained by increasing stabilizations of the triplet transition state. However, the "negative" barrier in R, that is , the fact that the stable ground state of R is non-polnar and that the planar conformation represents the transition state for rotation requires a different a explanation , the difference between Q and R is presumbly due to the steric intraction of explanation of the four chlorine substituents in the polar conformation of R. This situation resembles that in o,o'- tetrasubstituted biphenyls to alkenes with low or " negativee" barriers.