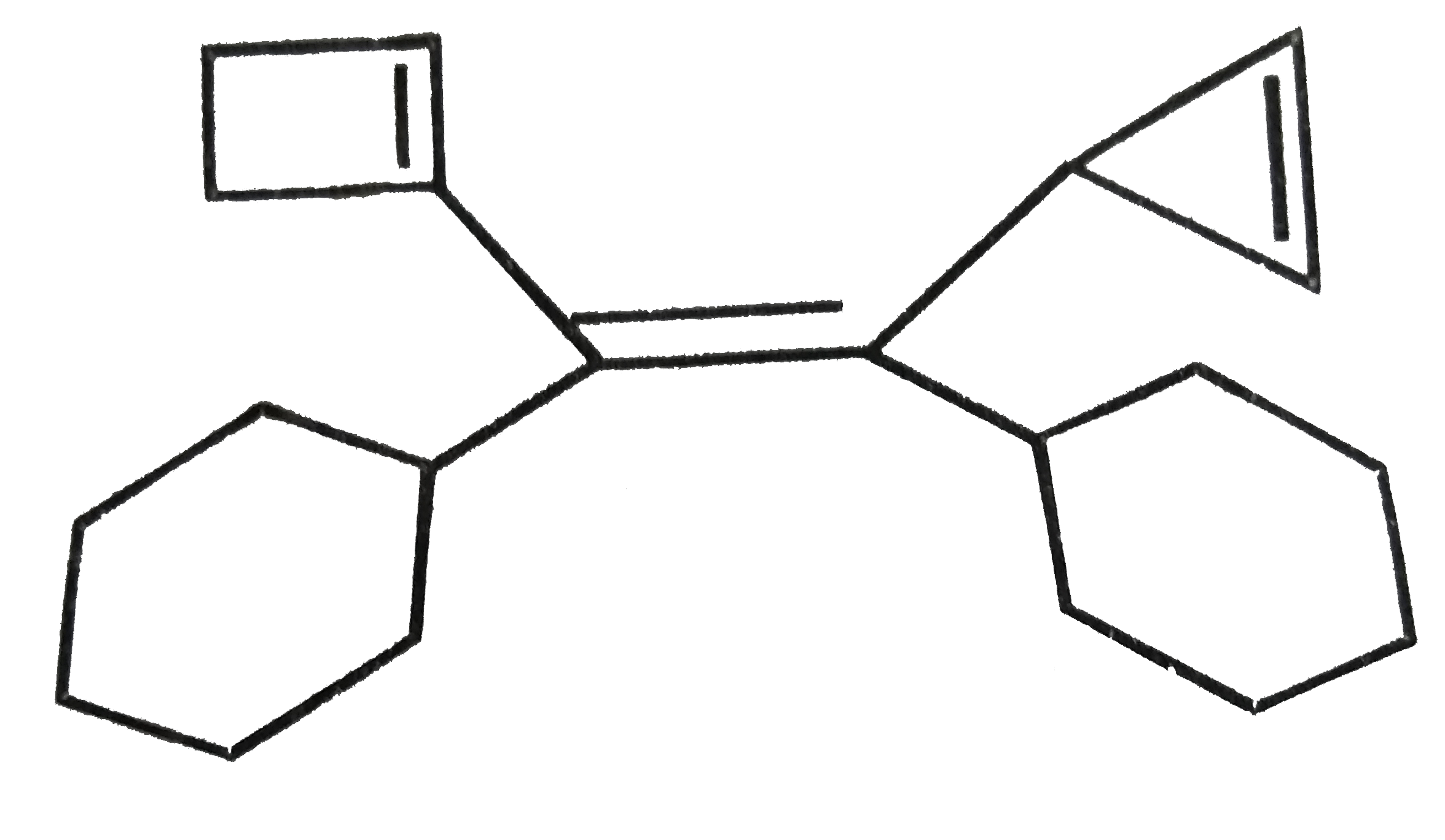
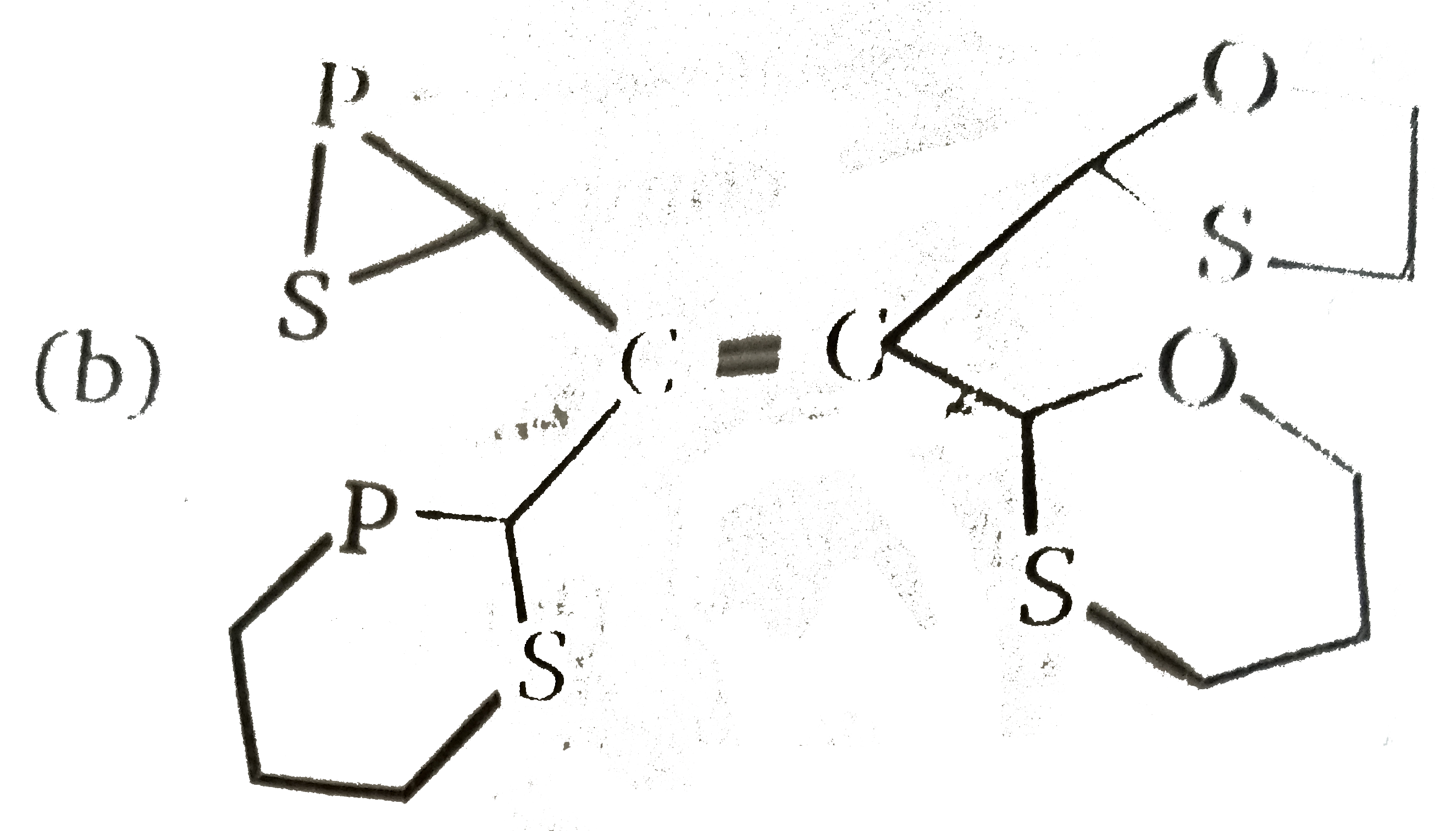
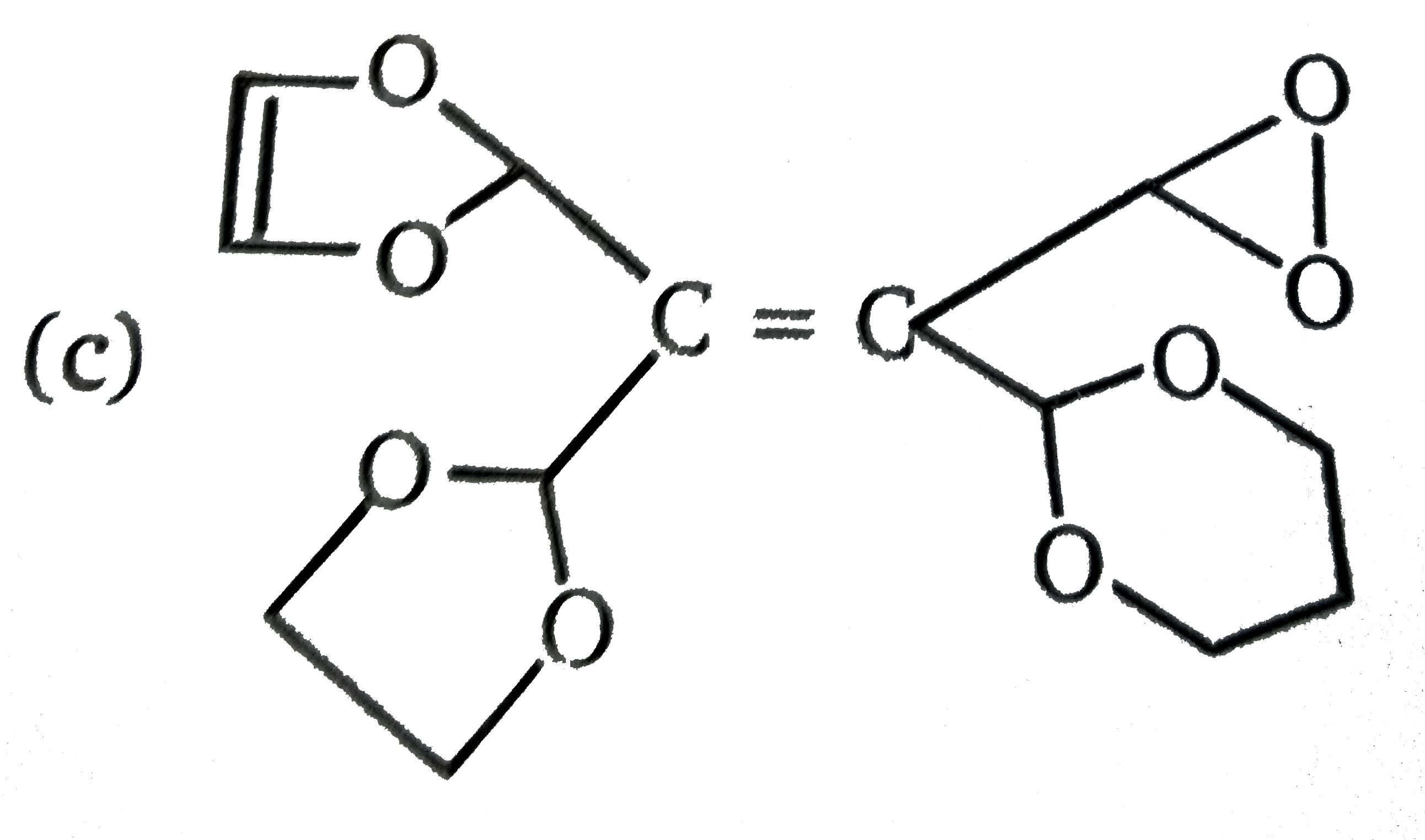
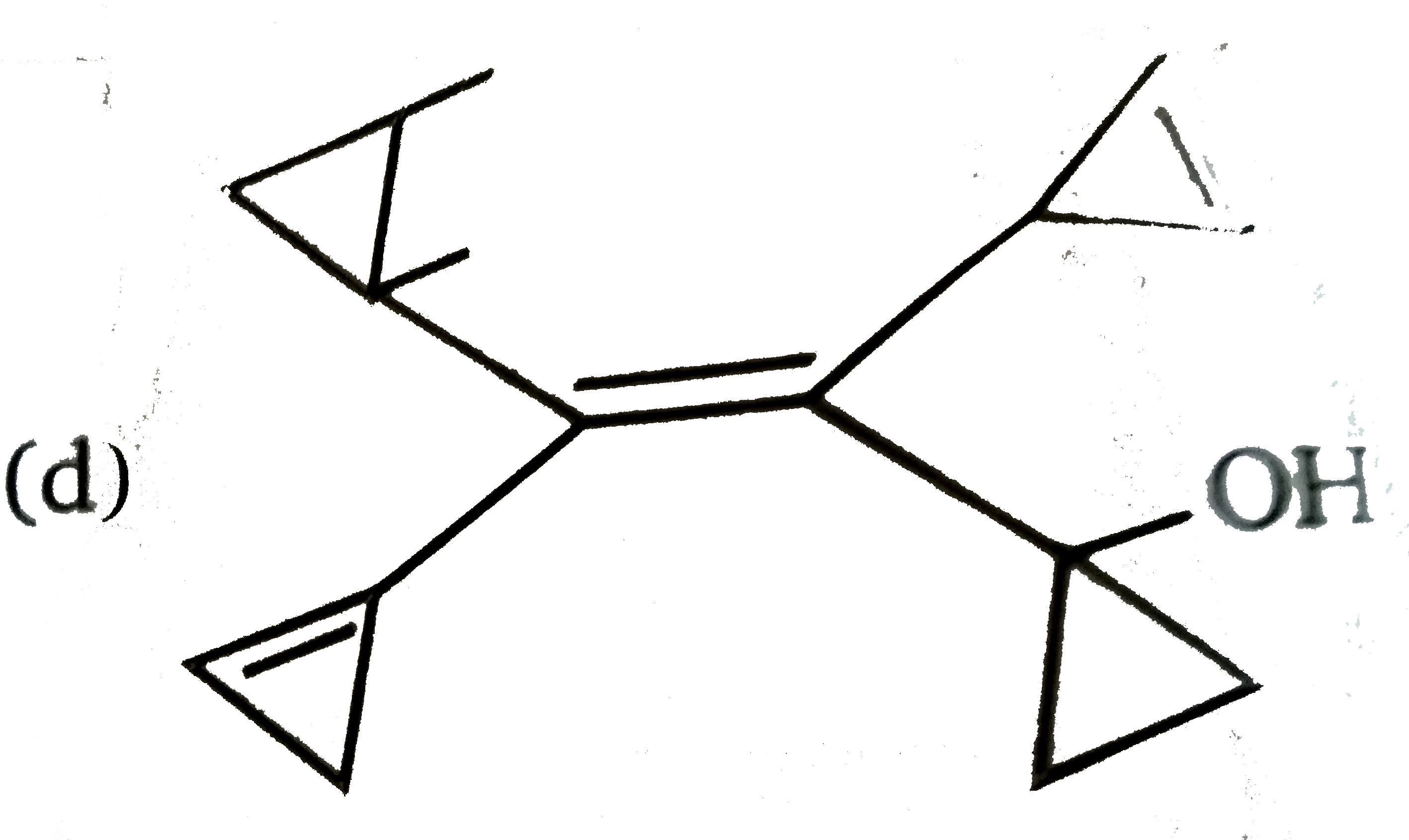
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ISOMERISM (STRUCTURAL & STEREOISOMERISM)
MS CHOUHAN|Exercise Level 1 (Q.1 To Q.30)|13 VideosISOMERISM (STRUCTURAL & STEREOISOMERISM)
MS CHOUHAN|Exercise Level 1 (Q.31 To Q.60)|9 VideosGRIGNARD REAGENTS
MS CHOUHAN|Exercise Level 1 (Q.61 To Q.66)|1 VideosNOMENCLATURE AND CONFORMATIONS OF ALKANES AND CYCLOALKANES
MS CHOUHAN|Exercise Additional Objective Questions (MCQ)|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MS CHOUHAN-ISOMERISM (STRUCTURAL & STEREOISOMERISM)-Subjective Problems
- Which of the following is E isomer ?
Text Solution
|
- Number of chiral isomers are:
Text Solution
|
Text Solution
|
- Sum of number of stereoisomer (C ) Degree of unsaturations in (D).
Text Solution
|
- How many 5 membered parent chain akane are possible for C(7)H(16)?
Text Solution
|
- Theoretical possible geometrical isomer of
Text Solution
|
- Total number of possible structural isomers of C(5)H(11)Br.
Text Solution
|
- Total number of plane of symmetry present in given compound is
Text Solution
|
- Total number of isomers for C(4)H(6)Br(2) containing cyclobutane ring ...
Text Solution
|
- Total number of structural isomer of C(9)H(18) containg cyclohexane ri...
Text Solution
|
- How many structural isomer are possible for C(4)H(10)O (only alcohol).
Text Solution
|
- Number of structural isomer of C(6)H(14) is .
Text Solution
|
Text Solution
|
- Find out the total number of stereocentre in the given compound. CH(...
Text Solution
|
- Find out the total number of stereoisomers of the given following comp...
Text Solution
|
- Find the total numberof isomers of C(7)H(14) (only 5-membered ring.)
Text Solution
|
- x= number of compound which undergoes Tautomerisation ot from an Aroma...
Text Solution
|
- If molecules is pyramidal, X stereoisomers are possible for : " ...
Text Solution
|