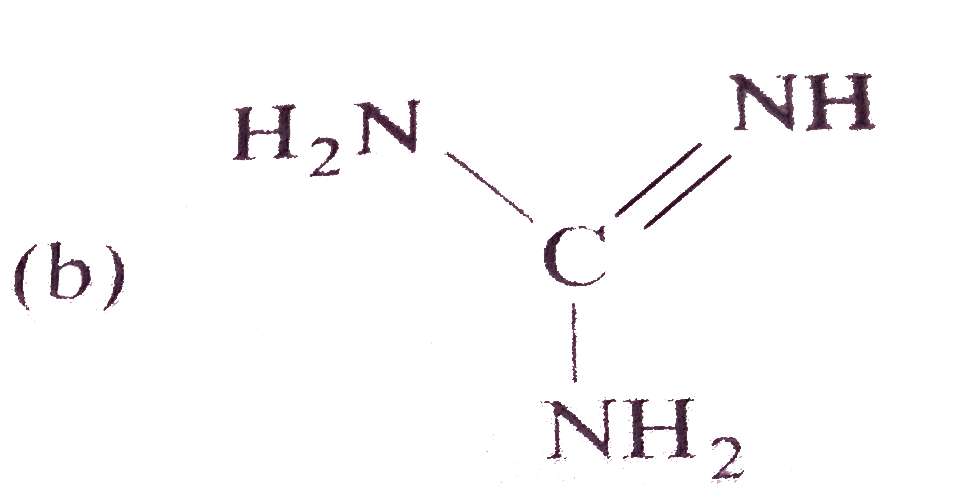
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
HIMANSHU PANDEY|Exercise Level 1 (Q.26 To Q.49)|24 VideosGENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
HIMANSHU PANDEY|Exercise Level 2 (Q.1 To Q.25)|25 VideosCHEMISTRY IN DAILY LIFE
HIMANSHU PANDEY|Exercise Integer Answer Type Problems|7 VideosHALIDES
HIMANSHU PANDEY|Exercise Subjective Type Problems|10 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
HIMANSHU PANDEY-GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-Subjective Type Problems
- The strongest base is :
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following systems are conjugated?
Text Solution
|
- Draw all reasonable resonance structures for each species.
Text Solution
|
- Draw all reasonable resonance structures for each species.
Text Solution
|
- Determine the hybridization at the carbon atom indicated in each speci...
Text Solution
|
- Explain each statement using resonance theory. (a) The indicated C-...
Text Solution
|
- Rank the following dienes in order of increasin heat of hydrogenation.
Text Solution
|
- How many pi electrons are contained in each molecule ?
Text Solution
|
- Which compaounds are aromatic? For any compound that is not aromatic, ...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following heterocycles are aromatic?
Text Solution
|
- Lebel each compound as aromatic, antiaromatic, or not aromatic. Assume...
Text Solution
|
- Hydrocarbons A and B both possess a significant dipolel, even though e...
Text Solution
|
- Rank the indicated C-C bonds in order of increasing bond length, and e...
Text Solution
|
- The purine heterocycle occurs commonly in the structure of DNA. (a) ...
Text Solution
|
- (a) How many pi electrons does C contion? (b) How many pi electrons ...
Text Solution
|
- Draw additional resonance structure for each species.
Text Solution
|
- The carbon-carbon bond lengths in naphthalene are not equal. Use a res...
Text Solution
|
- Which compound in each pair is the stronger acid?
Text Solution
|
- Treatment of indene with NaNH(2) forms its conjugate base in a Bronste...
Text Solution
|
- Draw the conjugate bases of pyrrole and cyclopentadiene. Explain why t...
Text Solution
|