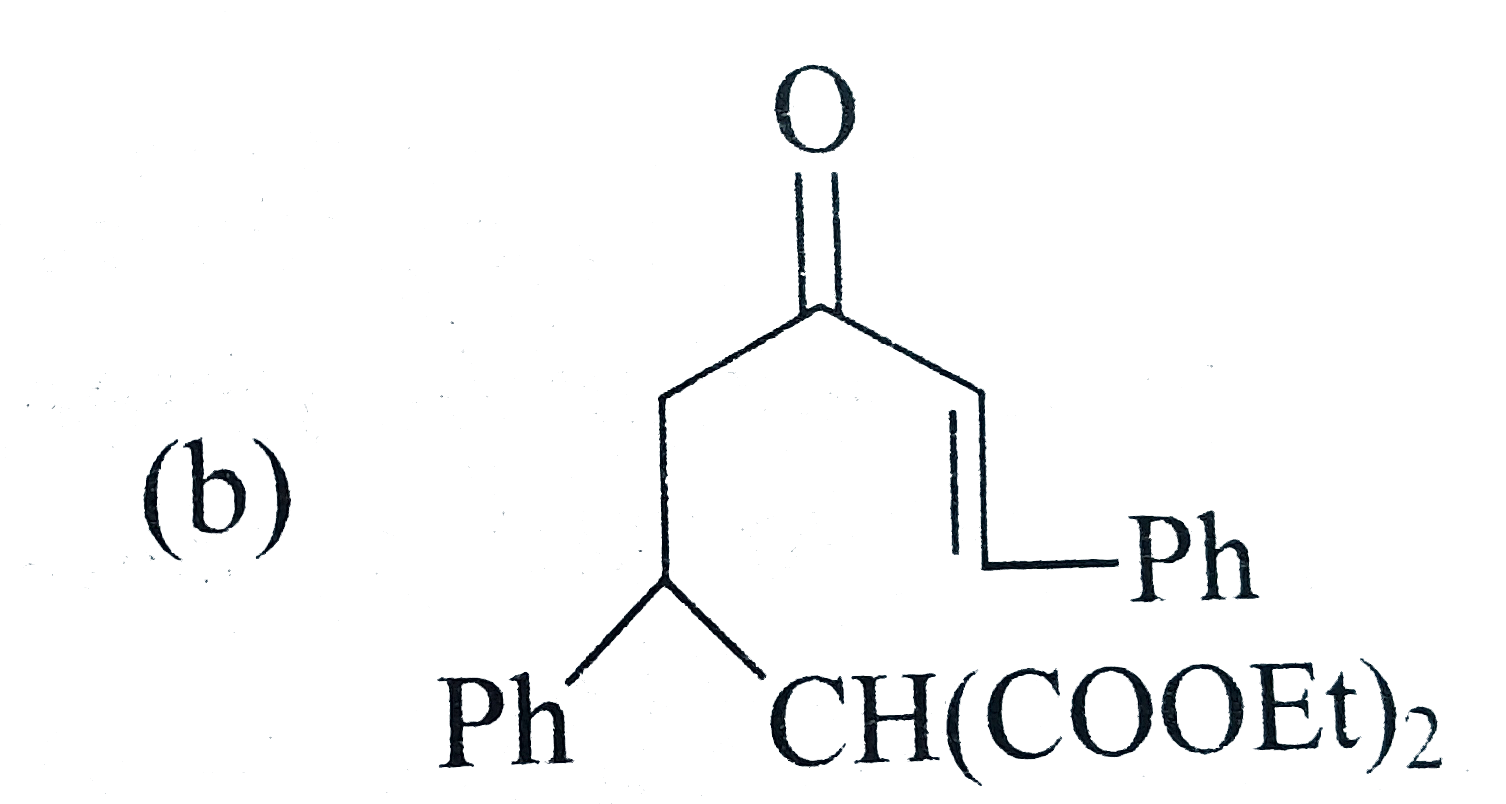
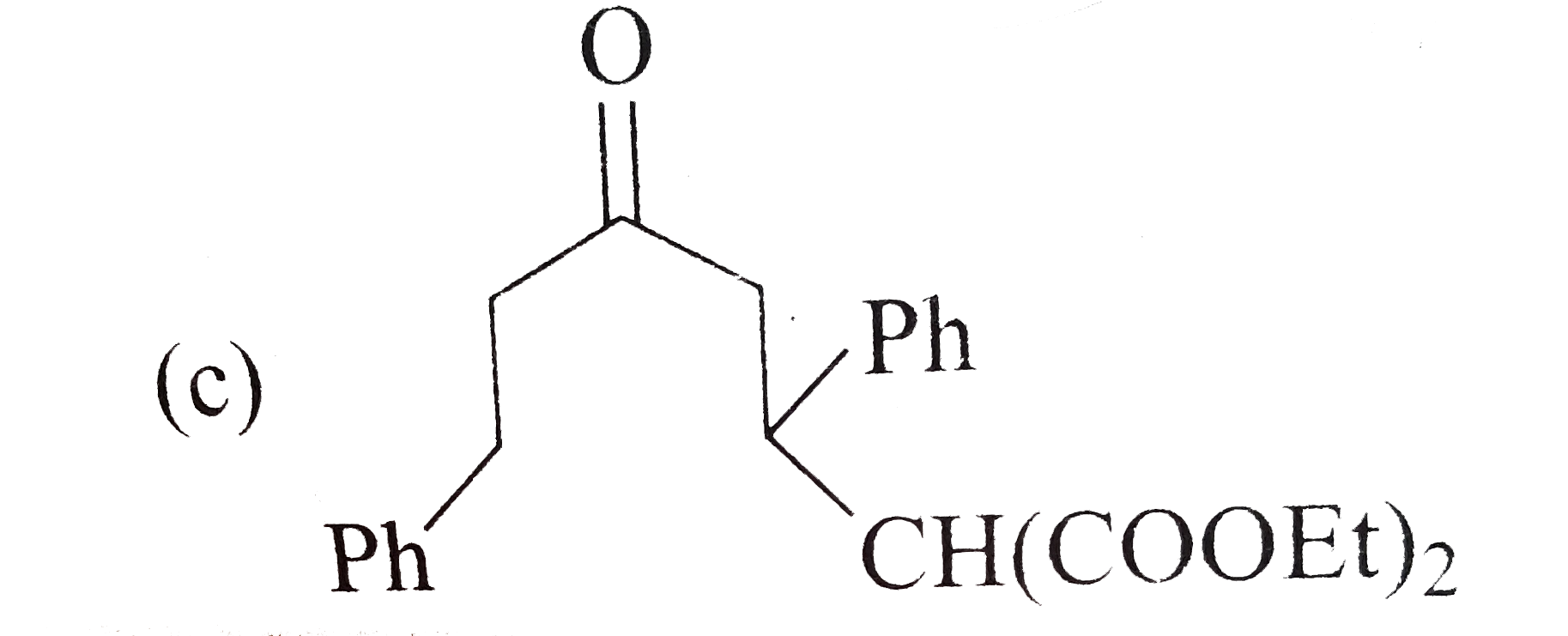
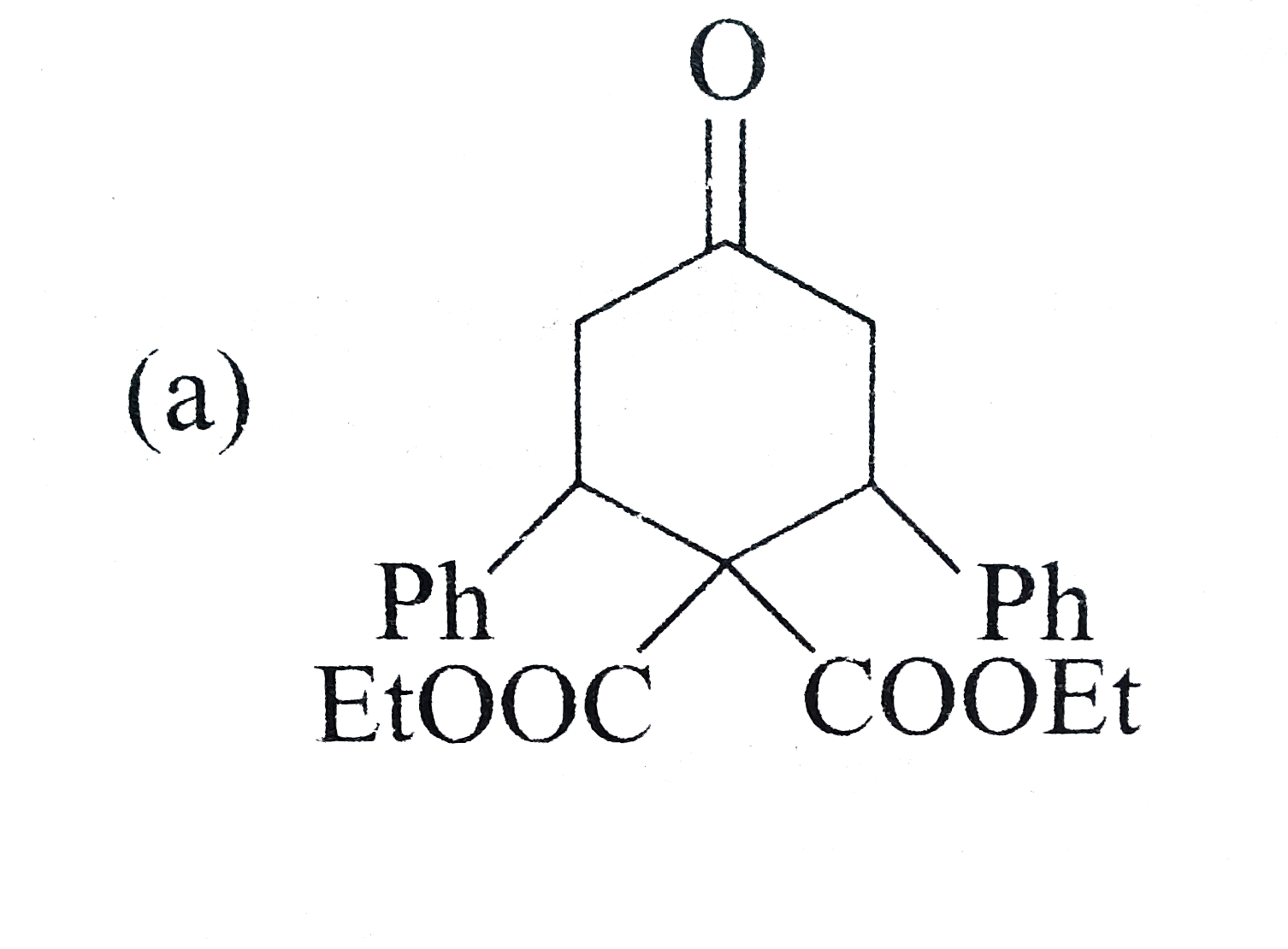A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CARBONYL COMPOUNDS
HIMANSHU PANDEY|Exercise Match The Column|11 VideosCARBONYL COMPOUNDS
HIMANSHU PANDEY|Exercise Integer Answer Type Problems|10 VideosCARBONYL COMPOUNDS
HIMANSHU PANDEY|Exercise Linked Comprehension Type (Q.1 To Q.25)|25 VideosCABOXYLIC ACIDS AND ITS DERIVATIVES
HIMANSHU PANDEY|Exercise Subjective Type Problems|8 VideosCHEMISTRY IN DAILY LIFE
HIMANSHU PANDEY|Exercise Integer Answer Type Problems|7 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
HIMANSHU PANDEY-CARBONYL COMPOUNDS-Linked Comprehension Type (Q.26 To Q.33)
- An organic compound (A) C(8)H(10)O was subjected to a series of test ...
Text Solution
|
- An organic compound (A) C(8)H(10)O was subjected to a series of test ...
Text Solution
|
- The base catalysed addition of a compound having active methylene grou...
Text Solution
|
- The base catalysed addition of a compound having active methylene grou...
Text Solution
|
- The base catalysed addition of a compound having active methylene grou...
Text Solution
|
- An organic compound (A), C(7)H(6)O gives positives test with Tollen's ...
Text Solution
|
- An organic compound (A), C(7)H(6)O gives positives test with Tollen's ...
Text Solution
|
- An organic compound (A), C(7)H(6)O gives positives test with Tollen's ...
Text Solution
|