Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MOTION-CENTRE OF MASS-Exercise - 4 Level-II
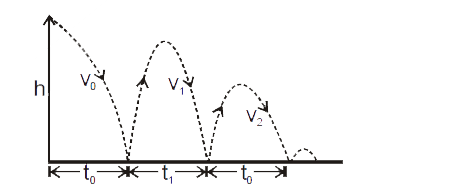
- A ball is dropped from a height h on to a floor. If in each collision ...
Text Solution
|
- STATEMENT-l : In an elastic collision between two bodies, the relative...
Text Solution
|
- A particle moves in the X-Y plane under the influence of a force such ...
Text Solution
|
- Two balls having linear momenta vecp(1)=phati and vecp(2)=-phati, und...
Text Solution
|
- A small block of mass M moves on a frictionless surface of an incline...
Text Solution
|
- A small block of mass M moves on a frictionless surface of an incline...
Text Solution
|
- A small block of mass M moves on a frictionless surface of an incline...
Text Solution
|
- If the resultant of all the external forces acting on a system of part...
Text Solution
|
- Look at the drawing given in the figure which has been drawn with ink ...
Text Solution
|
- Two small particles of equal masses stant moving in opposite directio...
Text Solution
|
- There object A ,B and C are kept is a straing line a fritionlas horize...
Text Solution
|
- A point mass of 1 kg collides elastically with a stationary point mass...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass 0.2 kg rests on a vertical post of height 5 m. A bullet...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m is projected from the ground with an initial spee...
Text Solution
|
- A pulse of light of duration 100ns is absorbed completely by a small o...
Text Solution
|
- A tennis ball dropped on a barizoontal smooth surface , it because bac...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass M has a circular cut with a frictionless surface as sh...
Text Solution
|
- A flat plate is moving normal to its plane through a gas under the act...
Text Solution
|
- Consider regular polygons with number of sides n = 3, 4, 5 ...... as s...
Text Solution
|
- A spring-block system is resting on a frictionless floor as shown in t...
Text Solution
|
- A small particle of mass m moving inside a heavy, hollow and straight ...
Text Solution
|