A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MOTION-CENTRE OF MASS-Exercise - 1
- Two masses m and 2m are attached to two ends of an ideal spring as sho...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks A(3kg) and B(6kg) are connected by a spring of stiffness 51...
Text Solution
|
- The spring block system lies on a smooth horizontal surface. The free ...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 'm' is attached to a spring in natural length of sprin...
Text Solution
|
- A super-ball of mass m is to bounce elastically back and forth between...
Text Solution
|
- A force exerts an impulse I on a particle changing its speed from u to...
Text Solution
|
- A boy hits a baseball with a bat and imparts and impulse J to the ball...
Text Solution
|
- A system of two blocks A and B are connected by an inextensible massle...
Text Solution
|
- The position-time graph of a particle of mass 0.1 kg is shown. The imp...
Text Solution
|
- The magnitude of force (in Newtons) acting on a body varies with time ...
Text Solution
|
- An impulse vec(I) changes the velocity of a particle from vec(v)(1) to...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of masses 10 kg and 4 kg are connected by a spring of negli...
Text Solution
|
- A ball strikes a smooth horizontal ground at an angle of 45^(@) with t...
Text Solution
|
- In an inelastic collision-
Text Solution
|
- Two perfectly elastic balls of same mass m are moving with velocities ...
Text Solution
|
- When two bodies collide elastically, then
Text Solution
|
- A ball hits the floor and rebounds after an inelastic collision . In t...
Text Solution
|
- Six steel balls of identical size are lined up long a straight frictio...
Text Solution
|
- The bob of a simple pendulum of length l dropped from a horizontal pos...
Text Solution
|
- Two balls A and B having masses 1 kg and 2 kg, moving with speeds 21 m...
Text Solution
|
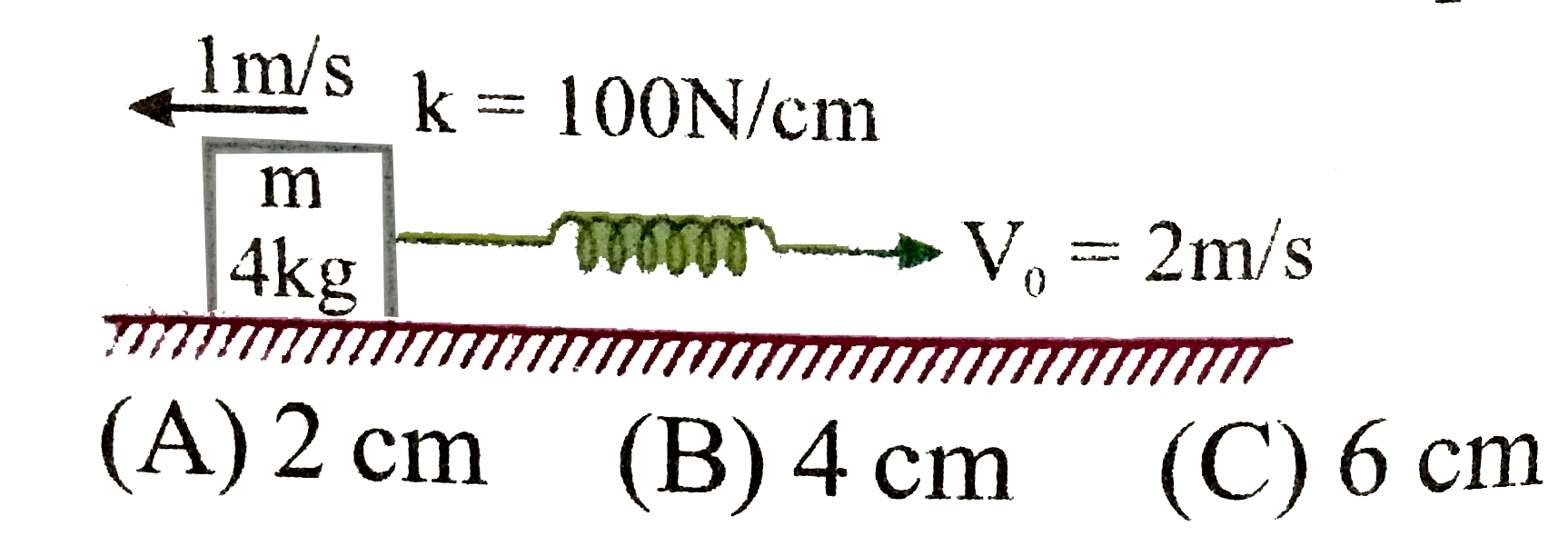 .
.