Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
SIMPLE HARONIC MOTION
MOTION|Exercise EXERCISE -1 ( SECTION-A )|8 VideosSIMPLE HARONIC MOTION
MOTION|Exercise EXERCISE -1 ( SECTION-B ) (Time per iod and angu larfrequency in SHM)|8 VideosSIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
MOTION|Exercise EXERCISE -3 Section - B Previous Year Problems | JEE MAIN|23 VideosSOUND WAVES
MOTION|Exercise Exercise - 3 (Section - B)|14 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MOTION-SIMPLE HARONIC MOTION -EXERCISE -4 (Leve-II) [ JEE 2011]
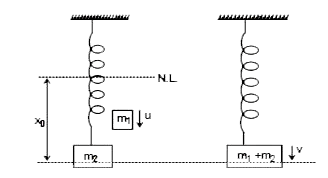
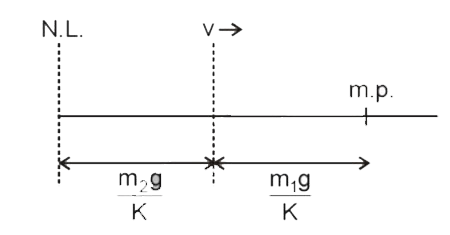
- Block of mass m(2) is in equilibrium and at rest. The mass m(1) moving...
Text Solution
|
- When a particle is mass m moves on the x- axis in a potential of the f...
Text Solution
|
- When a particle is mass m moves on the x- axis in a potential of the f...
Text Solution
|
- When a particle is mass m moves on the x- axis in a potential of the f...
Text Solution
|
- A point mass is subjected to two simultaneous sinusoidal displacement...
Text Solution
|
- A small block is connected to one end of a massless spring of un-stret...
Text Solution
|
- Phase space diagrams are useful tools in analysing all kond of dynamic...
Text Solution
|
- Phase space diagrams are useful tools in analysing all kond of dynamic...
Text Solution
|
- Phase space diagrams are useful tools in analysing all kond of dynamic...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m is attached to one end of a mass-less spring of f...
Text Solution
|
- Two independent harmonic oscillators of equal mass are oscillating abo...
Text Solution
|
- A block with mass (M) is connected by a massless spring with stiffness...
Text Solution
|