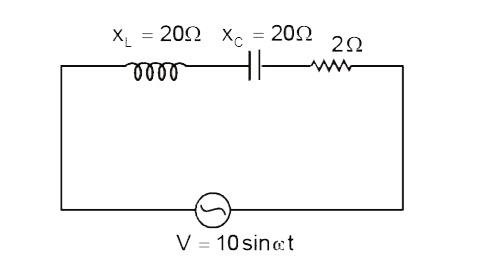
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MOTION-ALTERNATING CURRENT-EXERCISE - 4 (LEVEL - II)
- In following LCR circuit find Z, i(t), V(OC) , V(OL) at resonace frequ...
Text Solution
|
- In the given circuit the capacitor (C) may be charged through resistan...
Text Solution
|
- The capacitor of capacitance C can be charged (with the help of a resi...
Text Solution
|
- In the given circuit the capacitor (C) may be charged through resistan...
Text Solution
|
- An AC voltage source of variable angular frequency (omega) and fixed a...
Text Solution
|
- A sereis R-C circuit is connected to AC voltage source. Consider two c...
Text Solution
|
- A series R-C combination is connected to an AC voltage of angular freq...
Text Solution
|
- In the given circuit, the AC source has omega = 100 rad/s. Considering...
Text Solution
|
- A thermal power plant produed electric power of 600kW at 4000V, which ...
Text Solution
|
- A thermal power plant produed electric power of 600kW at 4000V, which ...
Text Solution
|
- At time t = 0, terminal A in the circuit shown in the figure is connec...
Text Solution
|
- Two inductors L(1)(inductors 1 mH, internal resistance 3 Omega) and L(...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown, L=1muH, C=1muF " and " R=1kOmega. They are conne...
Text Solution
|
- The instantaneous voltages at three terminals marked X, Y and Z are gi...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass 10^(-3) kg and charge 1.0 c is initially at rest At...
Text Solution
|